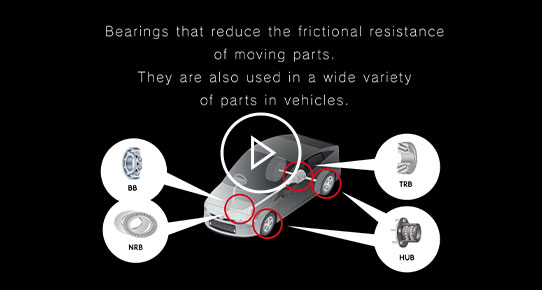
Steering system
Our Steering Systems Control the Car's Directional Functions and Hold the No. 1 Market Share
The vehicle is provided with basic functions such as running, turning and stopping. The steering system covers one of these basic functions, "turning."
The electric power steering system developed by JTEKT in 1988 first in the world is superior in fuel consumption as well as in the ease of installation and boasts the top share even now.

Steering principles
The driver manipulates the steering wheel, and its rotational movement is converted into a pushing-pulling motion of the tires by the gears, changing the direction of the tires.
In this process, hydraulic and motor power are used to assist the driver and reduce their burden.
Steering System Configuration
example:DP-EPS
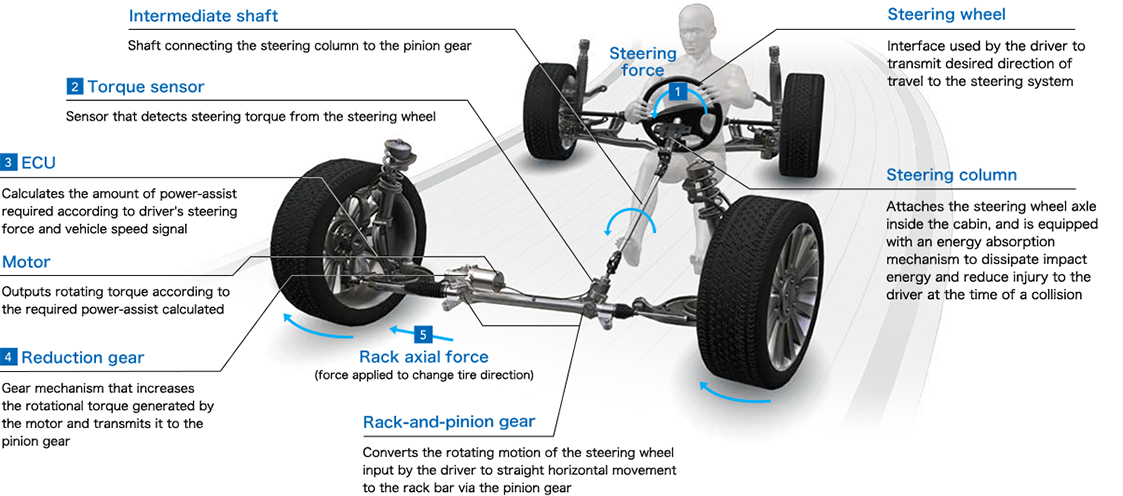
Basic steering operation
example:DP-EPS
-
1
Steering wheel is turned -
2
Torque sensor detects torque signal,which is then input into the ECU -
3
ECU adds electric current to the motor based on torque signal and vehicle speed
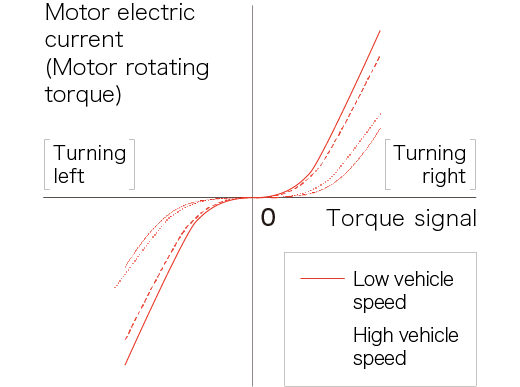
-
4
Motor rotating torque is increased by the reduction gear and transmitted to the pinion -
5
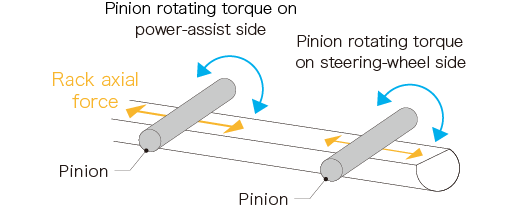
Pinion rotating torque (supplemental steering torque) on the power-assist side and pinion rotating torque (steering rotating torque) on the steering-wheel side are converted to rack axial force to change tire direction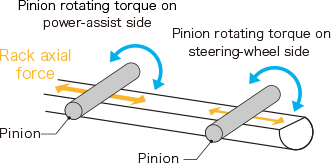
System Features by Type
・Column-assist
Since the motor and ECU are inside the cabin,waterproofing is not required and there is no influence on engine and transmission layout
Optimum steering system for compact vehicles with small rack force


・Rack-assistc
Excellent steering performance as the result of minimal friction between the time of turning the steering wheel and start of rack movement
Optimum steering system for medium-to large-sized vehicles that require better steering performance


An explanation of the latest technologies
In the near future, transformations will occur not in the vehicle society, but in the way we live as well
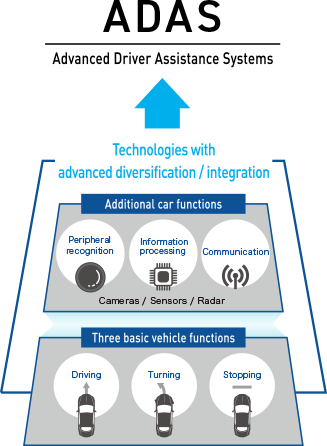
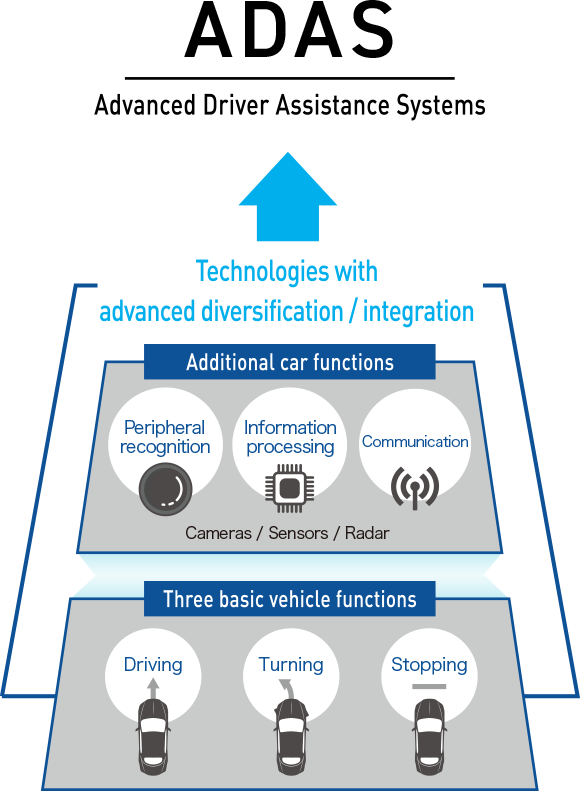
Thanks to higher computer processing capabilities and more accurate, inexpensive peripheral recognition sensors such as onboard radar and cameras, modern-day vehicles can detect the periphery and driving conditions with high precision. Accordingly, the practical application of active safety is advancing, perhaps best represented by collision avoidance braking.
Additionally, driver assistance systems openly using EPS control, such as automatic parking systems and lane departure warning/lane-keeping support systems, are contributing to the reduction of traffic accidents and the number of related fatalities. These systems are gradually becoming compulsory and are the focus of NCAP* ratings. As a result, their widespread use is anticipated.
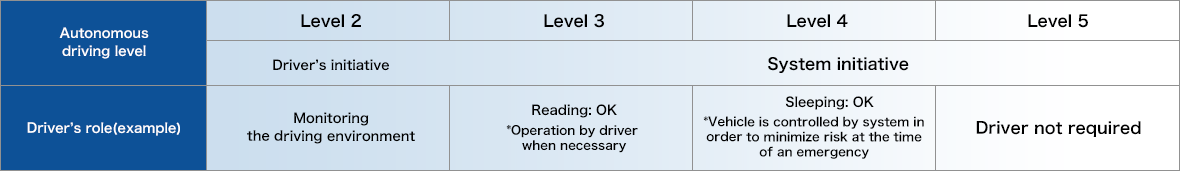
In regards to enhancing Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), the potential for further advancements from the current Level 2-3 status to fully autonomous driving systems that take over driver operation may be feasible with the expansion of applicable roads predicted for the future. Such technologies will not only transform the way we drive, but also how we live as well.
* NCAP (New Car Assessment Program)
A public vehicle collision test that involves crashing new cars and assessing the passenger safety level.
The Evolution of Steering Systems
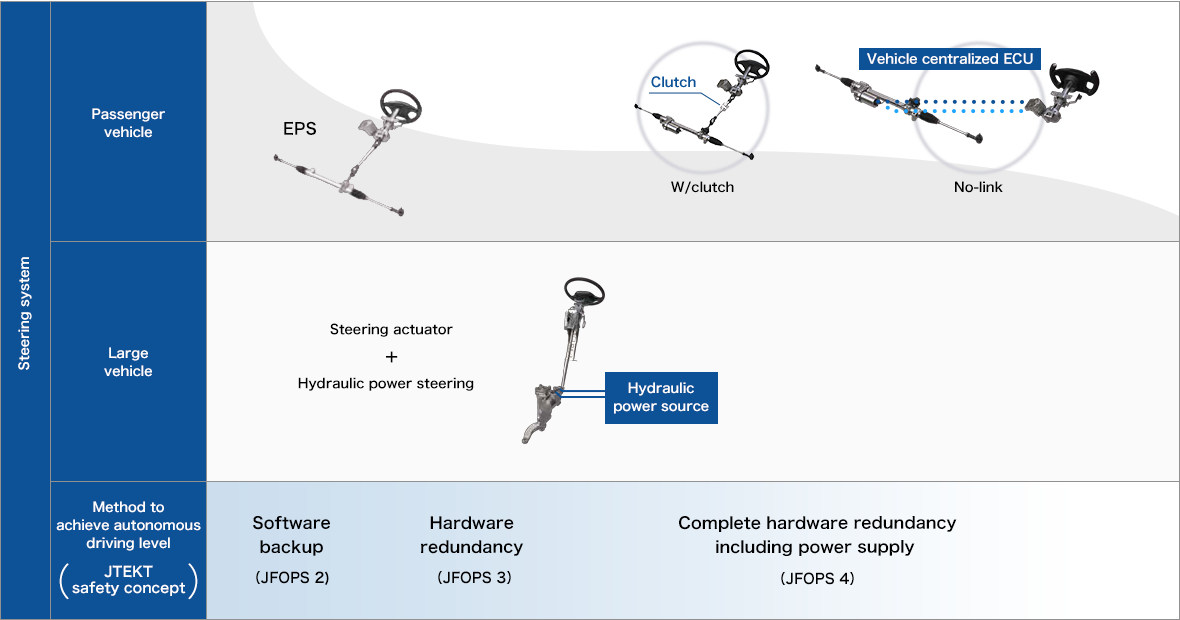
![[JFOPS] JTEKT Fail-OPerational System](/en/assets/images/field/automotive_aftermarket/steering/jfops_img.png) JTEKT concept of safety is defined from 0 to 4.
JTEKT concept of safety is defined from 0 to 4.
What is redundancy? By duplicating (making redundant) systems for functions required to have high reliability, safety is secured by the remaining functions even if a component of the system fails (redundant design).
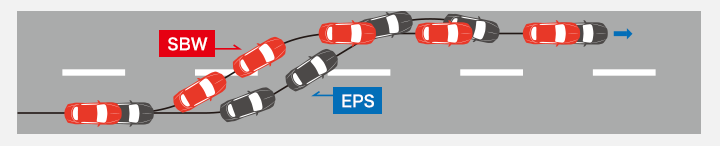
Merits of Steer-by-Wire
・Freedom in communication between the driver and system during ADAS operation(able to freely control both steering wheel and tires)
- 1.If collision avoidance operation is necessary, not only the steering wheel, but also the tire angle can be controlled appropriately.
- 2.Changes in vehicle orientation are reflected in steering wheel movement, providing steering sensation.
・Achieving ideal steering properties
1.Improved vehicle response/traceability/stability when changing lanes
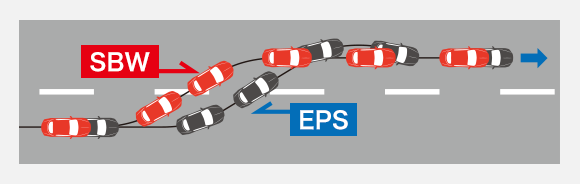
2.Improved handling at low speeds, improved driving stability at high speeds
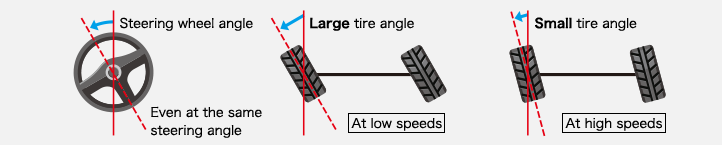
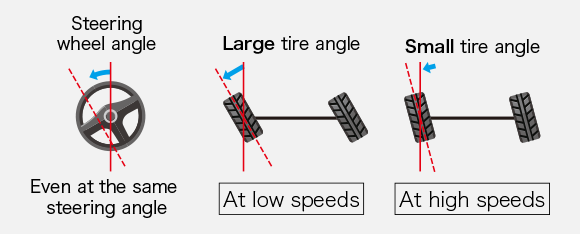
3.Conveys the necessary information from the road surface while blocking out disturbance, thus alleviating driver fatigue


・No-link SBW enables freedom of layout and contributes to expanding the vehicle interior space

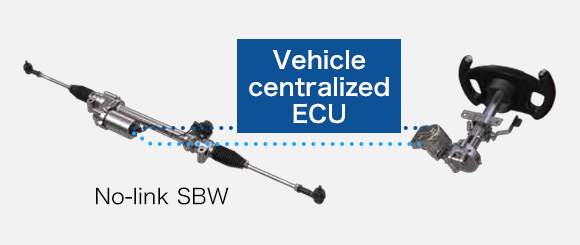
PRODUCT LINEUP
Electric power steerings
The steering system supports the driver in turning the steering wheel with an electric power assist unit consisting of a motor, controller, torque sensor and so on, thereby steering the tire.
In comparison with the hydraulic type that uses the engine of the vehicle as a power source, the electric type that uses the battery as a power source can improve the fuel consumption of the vehicle by 3 to 5%.
There are two types: column type with which the power assist unit is located in the column (inside the cabin) and rack type with which it is located in the engine room.
-


Column type electric power steering
Because the power assist unit is located in the cabin, this type of steering system is suitable for compact vehicles that have a smaller space in the engine room.
This type is adopted in principle for light, compact and medium cars.For more details...
-


Pinion type electric power steering
This steering system is provided with a power assist unit at the pinion shaft (inside the engine room) and it features calmness when compared with the column type.
For more details...
-
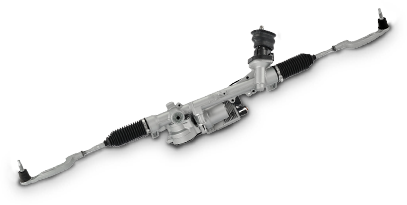
Dual pinion type electric power steering
Because the assist function of this steering system is separated from the steering wheel shaft, the degree of freedom of installation is enhanced and, together with an optimum strength design, a large output is realized.
For more details...
-

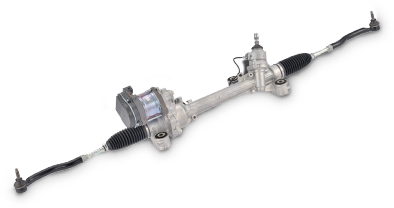
Rack parallel type electric power steering
This steering system, realizing both higher output and easier installation thanks for compact reduction gear and ball screw configuration, provides excellent safety, comfort and environmental performance.
For more details...
-

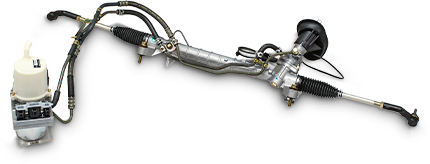
Electric pump type hydraulic power steering
This is an energy-saving hydraulic power steering system with which the hydraulic pump is driven under microcomputer control.
With idle stop mode support, the energy consumption in the non-steering mode (in straight-ahead travel) is reduced by about 80% (10-15 mode) when compared in horsepower.For more details...
-


Rack direct drive type electric power steering
Because the rack shaft is directly assisted, low friction, low inertia and ideal steering feel are realized.
Hydraulic power steerings
The hydraulic power assist unit supports the driver in turning the steering wheel, thereby steering the tire.
The system is compact and superior in the steering performance, capable of issuing a large output.
-
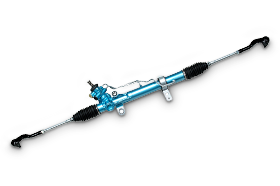
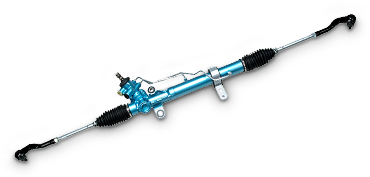
Rack direct drive type electric power steering
Because the rack shaft is directly assisted, low friction, low inertia and ideal steering feel are realized.
For more details...
-


Electronically controlled type hydraulic power steering
The hydraulic steering system and electronic control realize an ideal steering feel matching the vehicle speed.
-


Ball screw type manual power steering
The hydraulic power provides large-output and enhanced follow-up capability and natural power assistance.
The system features a high power and smooth steering feel even for trucks and buses.
Unit component
Various components supporting the steering system are introduced.
-


Power steering pump/Hydraulic hose/Reservoir tank
A pump generating a hydraulic power needed for the hydraulic steering system, transmission hose, reservoir tank and other components are provided in an optimized system.
Aftermarket-targeted
products -

Steering column
Supports energy absorption at tilting and telescopic motions as well as at collision.
-

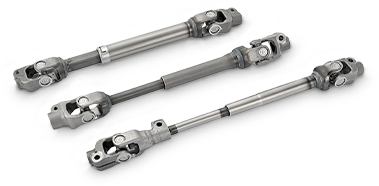
Intermediate shafts
A linkage shaft between the steering wheel and steering gear needs large torsional rigidity.
The gap at the joint and slide is reduced, reserving calmness even during travel on rough terrains.