Bearing Trivia
Bearing Failure (Part 1): "Failure" and "damage"
- #3 Bearing Failure
When designing a machine, it is important to select the bearing that is right for that machine.
In earlier "Bearing Trivia" columns, we showed you how to select the right bearing.
How to Select the Right Bearing (Part 1)
If you have selected your bearings properly and they are operated under ideal conditions, they will last until their specified service life comes to an end. But sometimes bearing failure can occur earlier than expected.
In this series, we will call bearing visual defects "bearing failure," and we will explain the typical bearing failure, its causes, and countermeasures that can be taken.
Please note that while the JTEKT rolling bearing catalog uses the terms "bearing" and "rolling bearing" interchangeably, this column does not use the term "rolling bearing" as a general rule.
1. What is bearing service life?
When a bearing that suppors a load rotates, the load is repeatedly applied to the raceway surfaces of the inner and outer rings each time rolling elements (balls or rollers) pass (see Figure 1).
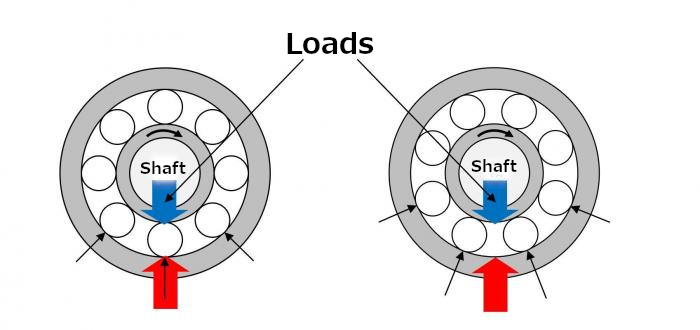
Fig. 1: Repeated loads applied to bearings
Due to this repeated load, high pressure is generated on the raceway surfaces of the inner and outer rings that are in contact with the rolling surfaces of the rolling elements.
Consequently, material flakes from the surfaces of the bearing rings or rolling elements by fatigue arising from repeated contact stress. This is called "flaking" or "spalling" (see Figures 2 and 3).
We will be giving detailed information on flaking in "Bearing Failure (Part 2)."
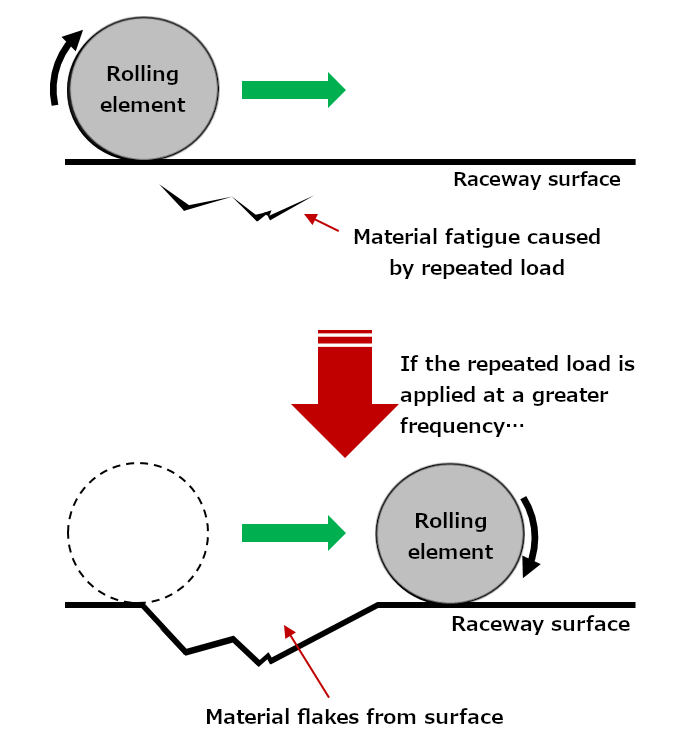
Fig. 2: Fatigue on the raceway surface
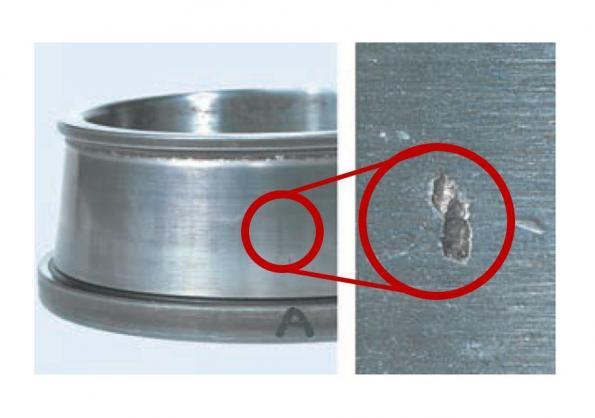

Fig. 3: Flaking (spalling)
(Inner ring raceway surface of a tapered roller bearing)
Rolling fatigue in the material leads to bearing failure. If the bearing has been operated under ideal conditions, the point at which this flaking occurs is the end of the bearing's service life.
See the following for details:
How to Select the Right Bearing (Part 3)
Bearing Trivia for Beginners 2: "Bearing Materials (Part 1: General Information)"
But sometimes a bearing can show abnormalities earlier than expected, and this is called "breakdown."
Table 1 shows the causes of bearing breakdown.
Table 1: The causes of bearing failure
| No. | Cause(s) |
| 1 |
Incorrect bearing selection |
| 2 |
Improper design and inaccuracy of the mounting parts |
| 3 |
Improper lubricant, lubrication method, or sealing device |
| 4 |
Insufficient consideration given to the rotational speed or operating temperature |
| 5 |
Carelessness or errors in the mounting process |
| 6 |
Entry of foreign matter either during mounting or while in operation |
| 7 |
Abnormal operating conditions (such as excessive load) |
In order to find the cause of a failure, it is necessary not only to investigate the bearing itself but to perform a comprehensive investigation that includes the lubricant and the mounting parts (shaft, housing, and surrounding components).
2. Bearing breakdown
1) Detecting abnormalities during bearing operation
Being able to identify and predict abnormalities that occur during operation (such as abnormal temperature rise, noise, or vibration) without taking the machine apart also greatly contributes to the productivity and economic efficiency of the machine.
Table 2 shows major types of detection of bearing abnormalities.
Table 2: The major types of detection of bearing abnormalities that occur during operation, and how to detect them
| No. | Method | What to confirm |
| 1 |
Temperature |
Abnormal temperature rise (monitored by means of a continuous record of the temperature; this method can only in used in relatively stable operating condition) |
| 2 |
Noise/Vibration |
Any noise/vibration made by the bearing (monitored by means of a stethoscope, vibration measuring instrument, or equivalent; accurate detection requires both training and a lot of practice) |
| 3 |
Lubricant |
Contamination, foreign matter, or metallic powder in a lubricant sample |
2) When and why bearing breakdown occurs
Before examining/considering the cause of the bearing breakdown, it is important first to have a proper grasp of just when the bearing breakdown occurred. As shown in Table 3, you can, to a certain extent, narrow down the cause of the bearing breakdown by determining when it occurred.
Table 3: When and why bearing breakdown occurs
| No. |
When the breakdown occurs |
Cause(s) | |||||
|
Selection* |
Mounting part* |
Lubrication* |
Defect* |
Mounting* |
Foreign matter* |
||
| 1 |
Immediately or shortly after bearing mounting |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 2 |
Immediately after regular disassembly and inspection of the bearing |
✔ | ✔ | ||||
| 3 |
Immediately after adding lubricant |
✔ | |||||
| 4 |
Immediately after repairing or replacing any of the surrounding components |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| 5 |
During normal operation |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
The following is an explanation of the various causes:
Selection Inappropriate bearing selection
Mounting parts Improper design and inaccuracy of the mounting parts (shaft, housing, and surrounding components)
Lubrication Improper lubricant, lubrication method, or amount of lubricant
Defect A defective bearing
Mounting Carelessness or errors in the mounting process
Foreign matter Defective sealing device, entry of foreign matter due to wear, etc., or 3) Abnormalities during bearing operation, their causes, and countermeasures that can be taken against them
3) Abnormalities during bearing operation, their causes, and countermeasures that can be taken against them
For abnormalities that occur during bearing operation, such as noise/vibration, abnormal temperature rise, and so on, we need to sort out the cause and countermeasures, and take the appropriate countermeasures. Table 4 shows some of the abnormalities that can occur during bearing operation, their causes, and countermeasures that can be taken against them.
Table 4: Abnormalities during bearing operation, their causes, and countermeasures
|
Abnormality |
Cause(s) |
Countermeasure(s) |
|
Temperature rise |
The internal clearance during operation is too small |
Adjust the interference and internal clearance of the bearing, and replace it with a new bearing |
|
Excessively heavy load |
Inspect and adjust the housing and remount the bearing |
|
|
Inappropriate amount of lubricant |
Reduce the amount of lubricant, or add more |
|
|
Excessively loud noise |
Flaws, brinelling, or nicks |
Replace the bearing with a new bearing, or repair it |
|
Entry of foreign matter |
Change the proper lubricant |
|
|
Excessive vibration |
Entry of foreign matter |
Change the proper lubricant |
|
Excessive bearing clearance |
Replace or reassemble the bearing |
For details on the causes and countermeasures for bearing abnormalities, please see the following:
Ball & Roller Bearings: Failures, Causes and Countermeasures
3. Bearing failure
1) The classification and terminology of bearing failure
Bearing "failure" refers to visual defects of the bearing.
As shown in Table 5, "failure" is divided into a number of classification shown in the "Classification of visual defect (general term)" column, and the details of these classifications are listed in the "Term(s) for the various types of failure (technical term[s])" column.
Table 5: Terms used to describe bearing failure
| Failure type | |
|
Classification of visual defect (general term) |
Term(s) for the various types of failure (technical term[s]) |
|
Rolling fatigue |
Flaking (spalling) |
|
Wear |
Wear, fretting |
|
Fracture |
Cracking, chipping |
|
Flaws |
Brinelling, nicks, scratching, scuffing |
|
Rust |
Rust, corrosion |
|
Seizure |
Seizure, discoloration, smearing |
|
Creep |
Creep |
|
Electric pitting |
Electric pitting |
2) Types of bearing failure and where they occur
Table 6 shows the types of bearing failure and where they occur. The names of the various bearing components are indicated in Figures 4 a) through 4 d).
Table 6: Types of bearing failure and where they occur
| No. |
Failure type |
Rings and rolling elements |
Rings |
Cage |
|||
|
Raceway surface and rolling surface |
Roller guide surface, cage guide surface, roller end face |
Other |
Fitting surface |
Pocket, guide surface |
Rivet |
||
| 1 |
Flaking (spalling) |
✔ | |||||
| 2 |
Wear |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
|
Fretting |
✔ | ✔ | |||||
| 3 |
Cracking |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
|
Chipping |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 4 |
Brinelling |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||
|
Nicks |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 5 |
Scratching |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
|
Scuffing |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| 6 |
Rust |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
|
Corrosion |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 7 |
Pear skin (speckles) |
✔ | |||||
|
Discoloration |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| 8 |
Smearing |
✔ | ✔ | ||||
| 9 |
Creep |
✔ | |||||
| 10 |
Electric pitting |
✔ | ✔ | ||||
| 11 |
Seizure |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 12 |
Cage damage |
✔ | ✔ | ||||
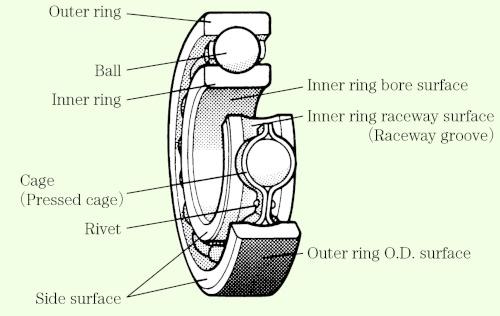
Fig. 4: a) Rolling bearing:Description of each partーDeep groove ball bearing
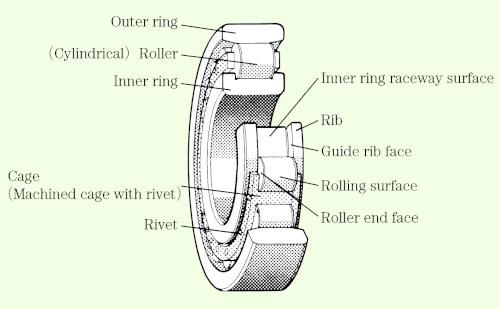
Fig. 4: b) Rolling bearing:Description of each partーCylindrical roller bearing
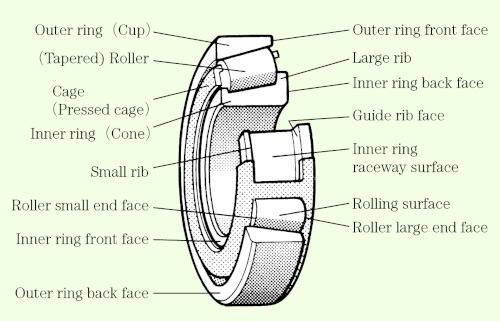
Fig. 4: c) Rolling bearing:Description of each partーTapered roller bearing
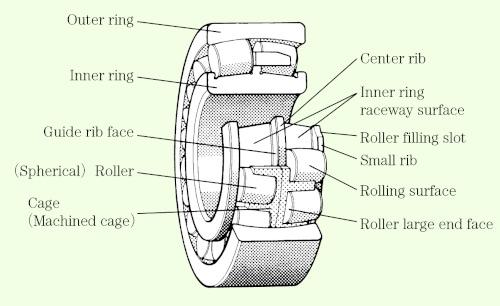
Fig. 4: d) Rolling bearing:Description of each partーSpherical roller bearing
See the following for details:
Ball & Roller Bearings: Failures, Causes and Countermeasures
4. Conclusion
If bearings are operated under ideal conditions, they will last until their service life comes to an end due to rolling fatigue of the materials. But sometimes bearings can break down, or "fail," earlier than expected, and, in such a situation, it is necessary not only to investigate the bearing itself but to perform a comprehensive investigation that includes the lubricant and the mounting parts (shaft, housing, and surrounding components).
In this column, "Bearing Failure (Part 1)," we conveyed the following points:
- By accurately ascertaining the time at which a bearing broke down, you can, to a certain extent, narrow down the cause of the failure.
- If a bearing has an abnormal operating condition, sorting out the cause of this abnormality can lead to effective countermeasures.
- Bearing "failure" refers to visual defects. We can classify the failure based on where it is on the bearing. This in turn leads to figuring out the cause of the bearing breakdown and more effective countermeasures.
- Note that when it comes to determining the cause of bearing breakdown, the following are all necessary:
• sufficient knowledge and experience regarding both bearings and lubrication;
• an awareness of the characteristics of the machine; and
• a familiarity with the bearing mounting conditions and operating history.
- If you have any technical questions regarding bearing failure, or opinions/thoughts on these "Bearing Trivia" pages, please feel free to contact us using the following form: