Bearing Trivia
How to Select the Right Bearing for Extreme Special Environments (EXSEV Bearings) (Part 2): Bearings for clean, vacuum, high-temperature, or corrosive environments
- #5 How to Select the EXSEV Bearing
In Part 1, we explained about the materials and lubricants used in bearings for extreme special environments.
How to Select the Right Bearing for Extreme Special Environments (EXSEV Bearings) (Part 1): Materials and lubricants
In this part, we will discuss important points for selecting bearings for extreme special environments used in clean, vacuum, high-temperature, or corrosive environments.
Note that because ball bearings are often used as rolling bearings for extreme special environments, this column uses ball bearings as an example.

1. Specifications of bearings for clean environments
Bearings made of high carbon chromium bearing steel cannot be used in most clean environments because they require anti-corrosion oil. For this reason, bearing rings (outer and inner rings) and balls are made of martensitic stainless steel (JIS SUS440C) used without applying anti-corrosion oil. Also, a lubricant with low particle emission is selected.
Figure 1 shows a list of bearings suitable for use in clean environments.
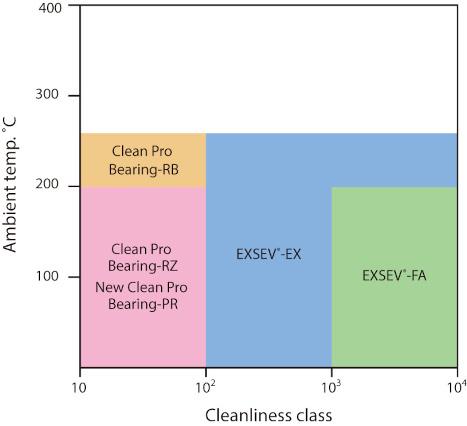
Figure 1: Bearings suitable for use in clean environments
Table 1 shows the specifications of each type of bearing.
Table 1: Specifications of bearings for clean environments
| Clean Pro Bearing-RZ | New Clean Pro Bearing-PR | Clean Pro Bearing-RB | EXSEV-EX | EXSEV-FA | ||
| List | ― | Figure 2 | ― | Figure 3 | Figure 4 | |
| Feature | Material | Stainless steel | ||||
| Lubrication | Polymeric solid lubricant | Grease | Polymeric solid lubricant | |||
| Outer ring | Martensitic stainless steel | |||||
| Inner ring | Martensitic stainless steel | |||||
| Ball | Martensitic stainless steel | |||||
| Cage | Austenitic stainless steel | Fluorocarbon resin | ||||
| Shield | Austenitic stainless steel | |||||
| Lubrication | Lubricant | Fluoropolymer coating | Fluorinated EXSEV-EX (Grease) | Fluoropolymer | ||
| Areas | Raceway surface, balls | Entire surface | Raceway surface, balls | Cage | ||
These bearings for clean environments generate less particles, making them suitable for clean environments.
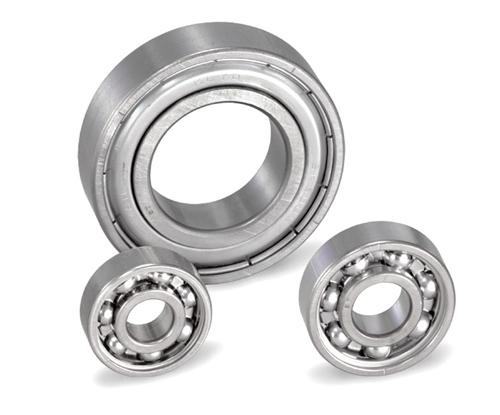

Figure 2: New Clean Pro Bearing-PR (polymeric solid lubricant coating)
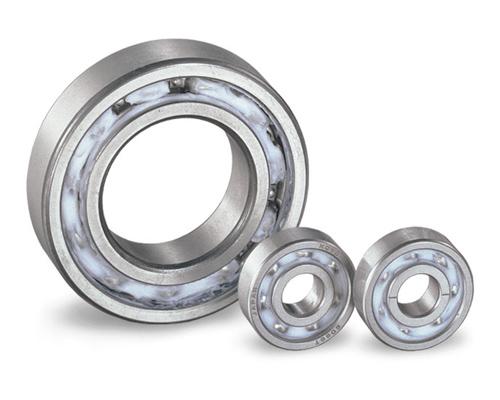 Figure 3: EXSEV-EX Bearing (fluorinated grease)
Figure 3: EXSEV-EX Bearing (fluorinated grease)
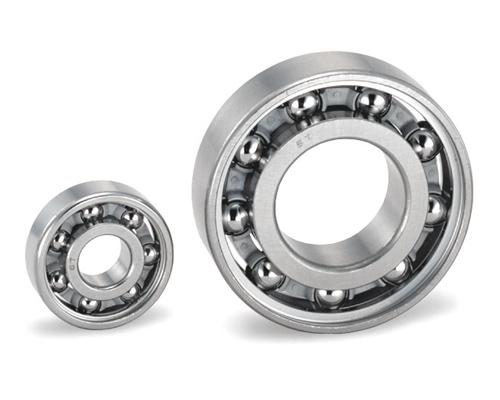 Figure 4: EXSEV-FA Bearing (fluorocarbon resin cage)
Figure 4: EXSEV-FA Bearing (fluorocarbon resin cage)
See the following for details on bearings for clean environments.
Clean environments
2. Specifications of bearings for vacuum environments
Martensitic stainless steel (JIS SUS440C) is used as the standard material for bearing rings and balls used in vacuums. Precipitation hardening stainless steel (JIS SUS630) is used when corrosion resistance is required, while high-speed tool steel (JIS SKH4, AISI M50, etc.) is used when high temperatures are involved. Ceramic materials with excellent heat and corrosion resistance are also used.
A bearing used in an ordinary vacuum chamber is repeatedly exposed to atmospheric air and vacuum. There is no rolling bearing lubricant that is effective for use under such a wide pressure range. Select a lubricant that is most suitable for the pressure and temperature that are normally used, and if necessary, based on the required cleanliness and corrosion resistance.
Figure 5 shows a list of bearings suitable for use in vacuum environments where cleanliness is not required.
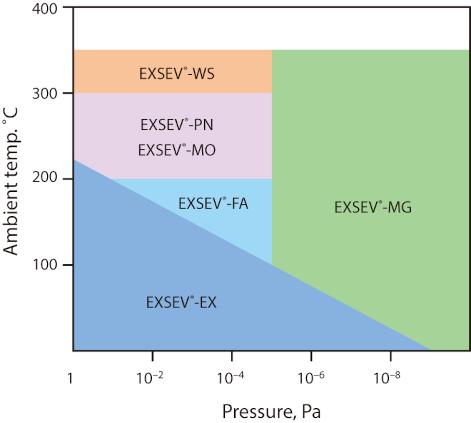
Figure 5: Bearings suitable for use in vacuum environments where cleanliness is not required
Table 2 shows the specifications of each type of bearing.
Table 2: Specifications of bearings for vacuum environments (when cleanliness is not required)
| EXSEV-EX | EXSEV-FA | EXSEV-WS | EXSEV-MG | EXSEV-PN | EXSEV-MO | ||
| List | ― | ― | Figure 6 | ― | ― | ― | |
| Feature | Material | Stainless steel | |||||
| Lubrication | Grease | Polymeric solid lubricant | Layer lattice-based solid lubricant | Soft metal-based solid lubricant | Polymeric solid lubricant | Layer lattice-based solid lubricant | |
| Outer ring | Martensitic stainless steel | ||||||
| Inner ring | Martensitic stainless steel | ||||||
| Ball | Martensitic stainless steel | ||||||
| Cage | Austenitic stainless steel | Fluorocarbon resin | ― | Austenitic stainless steel | PEEK resin | Austenitic stainless steel | |
|
Separator (*) |
― | ― | Including tungsten disulfide | ― | ― | ― | |
| Shield | Austenitic stainless steel | ||||||
| Lubrication | Lubricant | EXSEV-EX (grease) | Fluoropolymer | Tungsten disulfide | Silver | Molybdenum disulfide, etc. | Molybdenum disulfide |
| Areas | Cage | Separator | Ball | Cage | |||
(*) Separators are components that prevent direct contact between balls, as shown in Figure 7.
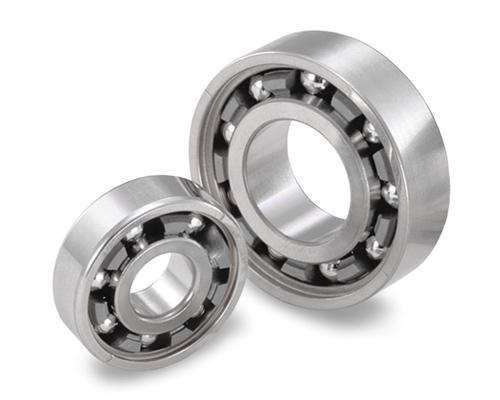 Figure 6: EXSEV-WS Bearing (separator including tungsten disulfide)
Figure 6: EXSEV-WS Bearing (separator including tungsten disulfide)
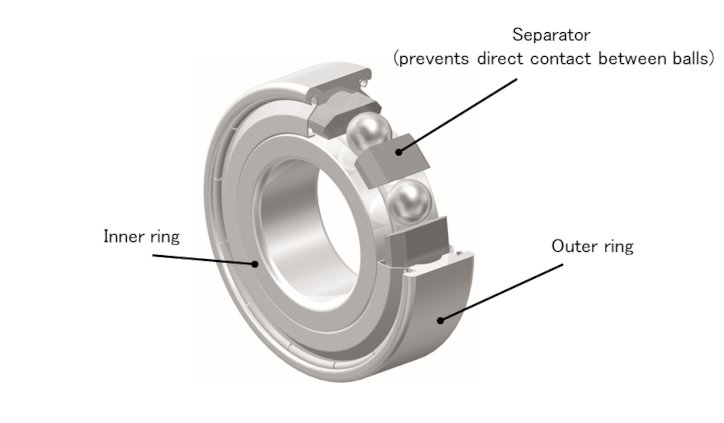
Figure 7: Separator
See the following for details on bearings for vacuum environments.
Vacuum environments
3. Specifications of bearings for high-temperature environments
Figure 8 shows bearing materials for high-temperature environments.
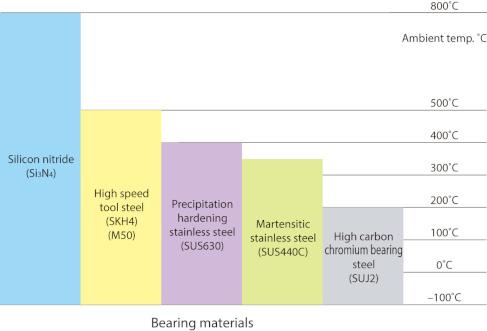
Figure 8: Bearing materials for high temperatures
Select a material suitable for the ambient temperature in which the bearing will be used.
| (1) | Ambient temperatures up to approx. 350°C Use martensitic stainless steel (JIS SUS440C). |
| (2) | Ambient temperatures between approx. 350 to 500°C Use High Temperature Hybrid Ceramic Bearings with bearing rings made of highly heat-resistant high-speed tool steel (JIS SKH4 or AISI M50) and rolling elements (balls) made of ceramic materials. |
| (3) | Ambient temperatures exceeding 500°C Use Full Complement Ceramic Ball Bearings. |
Figure 9 shows bearing lubricants for high-temperature environments.
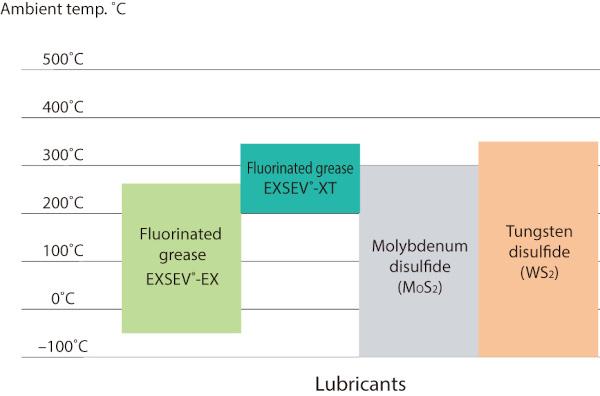
Figure 9: Lubricants for high temperatures
In ambient temperatures up to approx. 260°C, EXSEV-EX fluorinated grease can be used.
In ambient temperatures that exceed 260°C, EXSEV-XT fluorinated grease or layer lattice materials (molybdenum disulfide: MoS2 or tungsten disulfide: WS2) are to be used.
Because all layer lattice materials emit a large amount of particles, they are not suitable for applications where cleanliness is required.
Because there are no lubricants effective for use in ambient temperatures that exceed 500°C, unlubricated Full Complement Ceramic Ball Bearings are sometimes used.
Figure 10 shows the specifications of bearings for high-temperature environments.
Table 3 shows the specifications of Full Complement Ceramic Ball Bearings. For the specifications of bearings other than Full Ceramic Bearings, see Table 2.
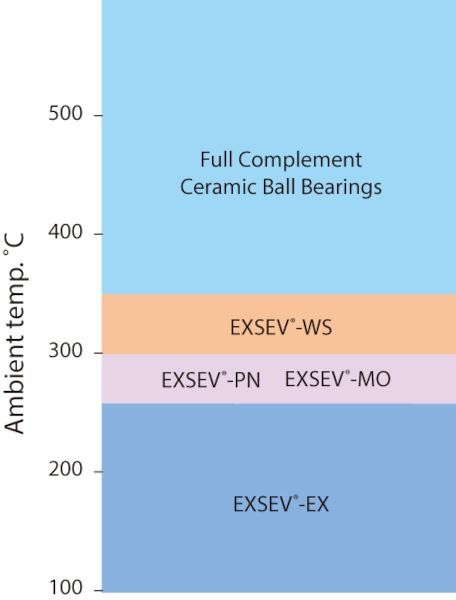
Figure 10: Bearings suitable for high temperatures
Table 3: Specifications of Full Complement Ceramic Ball Bearings"
| Full Complement Ceramic Ball Bearings | ||
| List | Figure 11 | |
| Feature | Material | Ceramic |
| Lubrication | None | |
| Outer ring | Silicon nitride | |
| Inner ring | Silicon nitride | |
| Ball | Silicon nitride | |
| Cage | (None) | |
| Shield | (None) | |
| Lubrication | Lubricant | (None) |
| Areas | ||
 Figure 11: Full Complement Ceramic Ball Bearing (uses silicon nitride)
Figure 11: Full Complement Ceramic Ball Bearing (uses silicon nitride)
See the following for details on bearings for high-temperature environments.
High-temperature environments
4. Specifications of bearings for corrosive environments
1) Corrosion resistance of special steels
Table 4 shows the corrosion resistance of special steels when subjected to common corrosive solutions.
Among stainless steels, JIS SUS630 exhibits better corrosion resistance than JIS SUS440C. However, stainless steel cannot be used in highly corrosive solutions such as acids and alkalis, or when trying to avoid rust caused by corrosion mixing with the solution.
Table 4: Corrosion resistance of special steels
| Solution | Concentration | 材質 | |||
| Martensitic stainless steel (JIS SUS440C) |
Precipitation hardening stainless steel (JIS SUS630) |
Austenitic stainless steel (JIS SUS304) |
High carbon chromium bearing steel (JIS SUJ2) |
||
| Tap water | - | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | × |
| Hydrochloric acid | 1% | △ | 〇 | 〇 | × |
| 10% | × | × | × | × | |
| Sulfuric acid | 1% | 〇 | ◎ | ◎ | × |
| 10% | △ | 〇 | 〇 | × | |
| Nitric acid | 20% | 〇 | ◎ | ◎ | × |
| Sodium hydroxide | 5% | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | △ |
| Seawater | - | 〇 | ◎ | ◎ | × |
Temperature: 25°C
Corrosion rate (mm/year) ◎: 0.125 or less, 〇: over 0.125 to 0.5, △: over 0.5 to 1.25, ×: over 1.25
2)Corrosion resistance of ceramic materials
Table 5 shows the corrosion resistance of ceramic materials. Although silicon nitride has excellent corrosion resistance and is a standard material used for ceramic bearings, it may corrode under conditions involving highly corrosive solutions or temperatures, etc. Zirconia and silicon carbide are to be used for such environments.
Table 5: Corrosion resistance of ceramic materials
| Solution | Material | ||
| Silicon nitride (Si3N4) |
Zirconia (ZrO2) |
Silicon carbide (SiC) |
|
| Hydrochloric acid | △ | 〇 | ◎ |
| Sulfuric acid | △ | 〇 | ◎ |
| Nitric acid | △ | 〇 | ◎ |
| Phosphoric acid | 〇 | 〇 | ◎ |
| Hydrofluoric acid | △ | × | ◎ |
| Sodium hydroxide | △ | 〇 | △ |
| Potassium hydroxide | △ | △ | △ |
| Sodium carbonate | △ | △ | △ |
| Sodium nitrate | △ | △ | △ |
| Water and saltwater | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ |
◎: Unaffected 〇: Mostly unaffected
△: May be slightly affected ×: May be affected
3) Specifications and applications of bearings for corrosive environments
Table 6 shows the specifications and main applications of common types of bearings used in corrosive environments.
Table 6: Specifications and main applications of common types of bearings used in corrosive environments
| Corrosion Guard Pro Bearing-SC | Ceramic Bearings | Corrosion Guard Pro Bearing-ZO | Corrosion Guard Pro Bearing-MD | ||
| List | Figure 12 | ― | Figure 13 | ― | |
| Feature | Material | Ceramic | Ceramic | Ceramic | Stainless steel + ceramic material |
| Lubrication | Polymeric solid lubricant | Polymeric solid lubricant | Layer lattice-based solid lubricant | Polymeric solid lubricant | |
| Outer ring | Silicon carbide | Silicon nitride | Zirconia | Precipitation hardening stainless steel | |
| Inner ring | Silicon carbide | Silicon nitride | Zirconia | Precipitation hardening stainless steel | |
| Ball | Silicon carbide | Silicon nitride | Zirconia | Silicon nitride | |
| Cage | Fluorocarbon resin | Fluorocarbon resin | PEEK resin | Fluorocarbon resin | |
| Shield | None | None | None | Austenitic stainless steel | |
| Lubrication | Lubricant | Fluoropolymer | Fluoropolymer | Molybdenum disulfide, etc. | Fluoropolymer |
| Areas | Cage | Cage | Cage | Cage | |
| Main applications | Strongly acidic Strongly alkaline Corrosive gas |
Weakly acidic Alkaline Reactive gas |
Saltwater Weakly acidic/alkaline |
Water Alkaline Reactive gas |
|
Using bearings for corrosive environments in a solution causes the solution itself to act as a lubricant for the bearing and significantly affects the service life of the bearing. Consult with JTEKT when selecting a bearing for such applications.
 Figure 12: Corrosion Guard Pro Bearing-SC (uses silicon carbide)
Figure 12: Corrosion Guard Pro Bearing-SC (uses silicon carbide)
 Figure 13: Corrosion Guard Pro Bearing-ZO (uses zirconia)
Figure 13: Corrosion Guard Pro Bearing-ZO (uses zirconia)
See the following for details on bearings for corrosive environments.
Corrosive environments
5. Conclusion
In this part, we discussed important points for selecting bearings for extreme special environments used in clean, vacuum, high-temperature, or corrosive environments.
| 1) | When selecting bearings for clean environments, select a bearing made of corrosion-resistant stainless steel that uses a lubricant with low particle emission. |
| 2) | When selecting bearings for vacuum environments, select a bearing made of stainless steel while considering corrosion resistance and heat resistance, if necessary. Select a lubricant based on the pressure and temperature that are normally used, and if necessary, based on the required cleanliness and corrosion resistance. |
| 3) | Select appropriate materials and lubricants for bearings for high-temperature environments based on the operating temperature. Because there are no lubricants effective for use in temperatures that exceed 500°C, Full Complement Ceramic Ball Bearings are suitable for use. |
| 4) |
When selecting bearings for corrosive environments, make sure to select one with excellent corrosion resistance. Note that when using bearings for corrosive environments in a solution, the solution acts as a lubricant for the bearing and significantly affects the service life of the bearing. Consult with JTEKT when selecting a bearing for such applications. |
These bearings for extreme special environments are used in the clean, vacuum, high-temperature, and corrosive environments of manufacturing equipment for semiconductors.
Product Series for Use in Semiconductor Manufacturing Processes
JTEKT also offers a selecting tool for bearings for extreme special environments.
Selecting tool for bearings for extreme special environments
In the next column, we will discuss important points for selecting bearings that require special properties such as non-magnetism, insulation, and high-speed rotation.
If you have any technical questions regarding bearings for extreme special environments, or opinions/thoughts on these "Bearing Trivia" pages, please feel free to contact us using the following form.