Bearing Trivia
Bearing Failure (Part 2): Causes and countermeasures for bearing failure (I)
- #3 Bearing Failure
In Part 1, we explained about bearing "breakdown" and "failure".
In this part, we will call bearing visual defects "bearing failure," and we will explain the characteristics of bearing failure, its typical causes, and countermeasures that can be taken.

Please note that while the JTEKT rolling bearing catalog uses the terms "bearing" and "rolling bearing" interchangeably, this column does not use the term "rolling bearing" as a general rule.
1. Types of bearing failure and where they occur
Table 1 shows the types of bearing failure and where they occur. Please refer back to Part 1 for the names of the various components of the bearing.
Table 1: Types of bearing failure and where they occur
| No. |
Failure type |
Rings and rolling elements |
Rings |
Cage |
|||
|
Raceway surface and rolling surface |
Roller guide surface, cage guide surface, roller end face |
Other |
Fitting surface |
Pocket, guide surface |
Rivet |
||
| 1 |
Flaking (spalling) |
✔ | |||||
| 2 |
Wear |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
|
Fretting |
✔ | ✔ | |||||
| 3 | Cracking | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
|
Chipping |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 4 |
Brinelling |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||
|
Nicks |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 5 |
Scratching |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
|
Scuffing |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| 6 |
Rust |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
|
Corrosion |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 7 |
Pear skin (speckles) |
✔ | |||||
|
Discoloration |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| 8 |
Smearing |
✔ | ✔ | ||||
| 9 |
Creep |
✔ | |||||
| 10 |
Electric pitting |
✔ | ✔ | ||||
| 11 |
Seizure |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 12 |
Cage damage |
✔ | ✔ | ||||
To see the names of all the various bearing components, please see the following:
2.Causes and countermeasures for bearing failure
In this part, from among the types of bearing failure listed in Table 1, we will explain the characteristics and the typical causes and countermeasures that can be taken for the following types:
- Flaking
- Wear and fretting
- Cracking and chipping
- Brinelling and nicks
- Scratching and scuffing
For a more detailed discussion of the causes and countermeasures, please see the following:
Causes and countermeasures: Ball & Roller Bearings Catalog
Failure examples: Ball & Roller Bearings: Failures, Causes and Countermeasures
1) Flaking (spalling)
"Flaking" refers to the phenomenon in which material flakes from the raceway surface and rolling element surface due to rolling fatigue (see Figures 1 a) and 1 b)). The point at which this phenomenon occurs is the end of the bearing's service life. However, if flaking occurs earlier than expected, this can be considered an abnormality, which requires an investigation regarding the cause and also requires countermeasures to be taken.
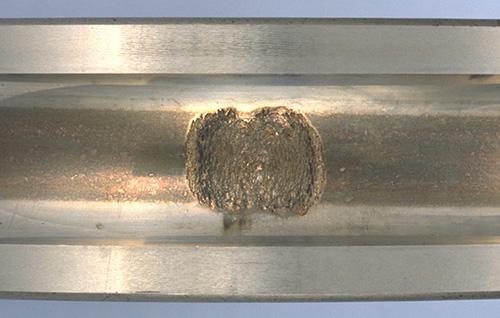
Fig. 1 a): Flaking (spalling) [inner ring of a deep groove ball bearing]

Fig. 1 b): Flaking (spalling) [inner ring of a cylindrical roller bearing]
[Reference]
One type of failure caused by rolling fatigue in the material is what is called "pitting."
This phenomenon involves tiny "cavities" with a depth of about 0.1 mm appearing on the raceway surface.
Table 2 shows the typical causes of, and countermeasures against, flaking (spalling).
Table 2: Typical flaking (spalling) causes and countermeasures
|
Flaking (spalling) condition |
Cause(s) |
Countermeasure(s) |
|
Occurring on one side of the raceway of a radial bearing
|
・ Abnormally excessive axial load |
・ For the fitting of the housing and the outer ring of the free side bearing, use a clearance fit |
|
Occurring symmetrically along the circumference of the raceway |
・Inaccurate housing roundness |
・Correct the processing accuracy of the housing bore (take particular care to ensure the processing accuracy for split housings) |
|
Occurring at an angle to the raceway of a radial bearing
|
・ Improper mounting |
・Improve the centering accuracy |
2) Wear and fretting
"Wear" occurs most frequently on sliding contact surfaces such as roller end faces and rib faces, cage pocket surfaces, and the guide surfaces of cages and bearing rings (see Figure 2 a)). Note, however, that wear caused by foreign matter or corrosion can affect not only sliding surfaces but also rolling surfaces (see Figure 2 b)).

Fig. 2 a): Wear [end faces of cylindrical rollers]
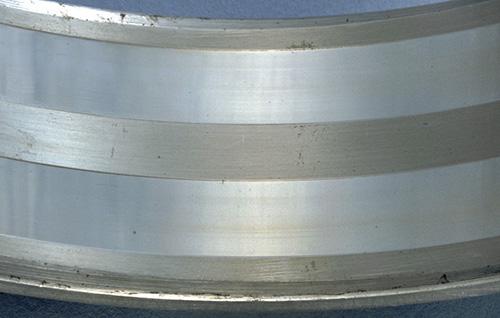
Fig. 2 b): Wear [outer ring raceway surface of a double-row cylindrical roller bearing]
Table 3 shows the typical causes of, and countermeasures against, wear.
Table 3: Typical wear causes and countermeasures
|
Wear condition |
Cause(s) |
Countermeasure(s) |
|
Occurring on a sliding contact surface |
・Improper or insufficient lubricant |
・ Reexamine the selection of lubricant or lubrication method ・ Improve the sealing device |
|
Occurring on a raceway surface or rolling surface |
・Entry of foreign matter |
"Fretting" refers to the phenomenon in which rust-colored wear particles develop on bearings that are subject to vibration while in a stationary condition (see Figures 3 a) and 3 b)).

Fig. 3 a): Fretting [inner ring bore surface of a tapered roller bearing]
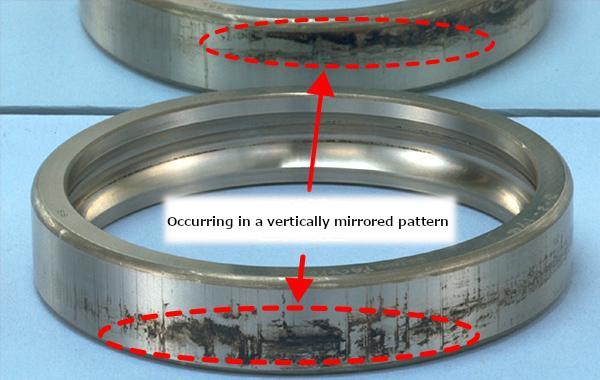
Fig. 3 b): Fretting [outer ring outside surface of a deep groove ball bearing]
Table 4 shows the typical causes of, and countermeasures against, fretting.
Table 4: Typical fretting causes and countermeasures
|
Fretting condition |
Cause(s) |
Countermeasure(s) |
|
Rust-colored wear particles on the fitting surfaces |
・Insufficient interference |
・Provide greater interference |
Since fretting on a raceway surface often looks similar to brinelling, it is sometimes called "false brinelling" (see Figure 4).

Fig. 4: False brinelling [inner ring raceway surface of a deep groove ball bearing]
Table 5 shows the typical causes of, and countermeasures against, false brinelling.
Table 5: Typical false brinelling causes and countermeasures
|
False brinelling condition |
Cause(s) |
Countermeasure(s) |
|
False brinelling at the same interval as the rolling element spacing |
・ Vibration and oscillation when the bearing is stationary |
・Improve the fixing method of the shaft and housing |
3) Cracking and chipping
"Cracking" is a collective name for things like splits and fractures. "Chipping," meanwhile, refers to defects that occur in a part of the rib of the bearing ring or in the corner of the roller. (See Figures 5 a) and 5 b).)

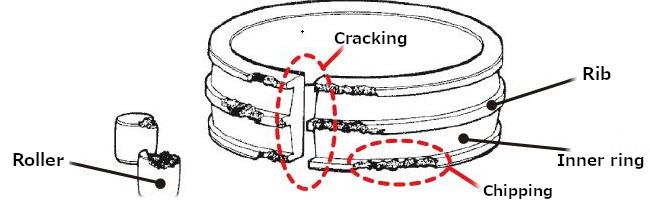
Fig. 5 a): Cracking and chipping [outer ring, inner ring, and roller of a spherical roller bearing]

Fig. 5 b): Chipping [outer ring rib of a cylindrical roller bearing]
Table 6 shows the typical causes of, and countermeasures against, cracking and chipping.
Table 6: Typical cracking and chipping causes and countermeasures
|
Cracking/Chipping condition |
Cause(s) |
Countermeasure(s) |
|
Cracking of the outer ring or inner ring |
・Excessive interference |
・Select a proper fit |
|
Chipping on the rib |
・ Impact on a rib during mounting |
・ Improve the mounting procedure |
4) Brinelling and nicks
"Brinelling" is a small surface indentation generated either (i) on the raceway surface through plastic deformation at the contact point between the raceway and rolling elements or (ii) on the rolling surfaces by the entry of foreign matter, when a heavy load is applied while the bearing is stationary or rotating at a low rotation speed (see Figures 6 a) and 6 b)). Nicks are those indentations produced directly by rough handling such as hammering.
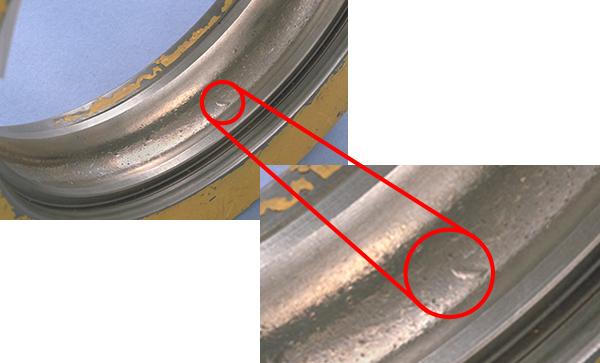
Fig. 6 a): Brinelling [outer ring raceway surface of a deep groove ball bearing]

Fig. 6 b): Brinelling [inner ring raceway surface of a tapered roller bearing]
Table 7 shows the typical causes of, and countermeasures against, brinelling and nicks.
Table 7: Typical brinelling and nick causes and countermeasures
|
Brinelling/Nick condition |
Cause(s) |
Countermeasure(s) |
|
Brinelling on the raceway at the same interval as the rolling element spacing |
・ Impact load during mounting |
・ Improve the mounting procedure |
|
Brinelling on a raceway surface or rolling surface |
・ Entry of foreign matter |
・ Clean the bearing and the area around it |
Scratching and scuffing
"Scratching" refers to the development of relatively shallow marks caused by sliding contact, in the same direction as the sliding, and they are not accompanied by apparent melting of material (see Figure 7 a)). "Scuffing" refers to marks whose surfaces are partially melted due to higher contact pressure producing a greater heat effect (see Figure 7 b)). In general, you can think of scuffing as a more severe form of scratching.
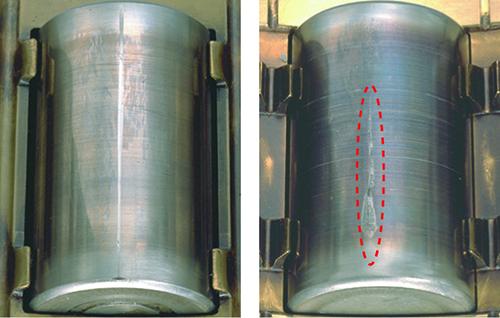
Fig. 7 a): Scratching [roller rolling surface of a cylindrical roller bearing (scratching in an axial direction)]

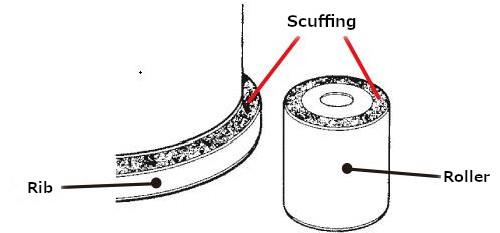
Fig. 7 b): Scuffing on a rib surface and roller end face [cylindrical roller bearing with a rib]
Table 8 shows the typical causes of, and countermeasures against, scratching and scuffing.
Table 8: Typical scratching and scuffing causes and countermeasures
|
Scratching/Scuffing condition |
Cause(s) |
Countermeasure(s) |
|
Scratching on a raceway surface or rolling surface |
・Insufficient lubricant at initial operation |
・Apply lubricant to the raceway and rolling surfaces when mounting |
|
Scuffing on the rib surface and roller end face |
・ Improper or insufficient lubricant |
・Reexamine the selection of lubricant or lubrication method |
Conclusion
1) In "Bearing Failure (Part 2)," from among the various types of bearing failure, we explained the characteristics and the typical causes and countermeasures that can be taken for the following types:
- Flaking
- Wear and fretting
- Cracking and chipping
- Brinelling and nicks
- Scratching and scuffing
2) When it comes to determining the cause of bearing breakdown, the following are all necessary:
- sufficient knowledge and experience regarding both bearings and lubrication;
- an awareness of the characteristics of the machine; and
- a familiarity with the bearing mounting conditions and operating history.
3) If you have any technical questions regarding bearing failure, or opinions/thoughts on these "Bearing Trivia" pages, please feel free to contact us using the following form:
4) In "Bearing Failure (Part 3)," from among the various types of bearing failure, we will explain the characteristics and the typical causes and countermeasures that can be taken for the following types:
- Rust and corrosion
- Pear skin and discoloration
- Smearing
- Creep
- Electric pitting
- Seizure
- Cage damage