Bearing Trivia
How to Select the Right Bearing for Extreme Special Environments (EXSEV Bearings) (Part 1): Materials and lubricants
- #5 How to Select the EXSEV Bearing
The use of conventional bearings may not be possible in special environments such as clean, vacuum, high-temperature, or corrosive environments, or with requirements of special properties such as non-magnetism, insulation, and high-speed rotation.
JTEKT has given its line of bearings designed to meet customer needs for extreme special environments the name "EXSEV bearings.

JTEKT has published a guide for selecting the right bearing for extreme special environments in its catalog EXSEV Bearings and CERAMIC Bearings for Extreme Special Environments, but the catalog uses a large number of technical terms and is very large, so many people seem to have trouble handling it.
That's where this column comes in. Here, we will explain the key points to consider when selecting your bearing for extreme special environments that is right for your machine.
In this column, we will also discuss ceramic bearings, which are often used in extreme special environments or when special properties are required.
The catalog EXSEV Bearings and CERAMIC Bearings for Extreme Special Environments uses the terms "bearing" and "rolling bearing" interchangeably. This column does not use the term "rolling bearing" as a general rule.
What are the criteria for selecting a bearing for extreme special environments?
Generally, when selecting from among the various types of available bearings the bearing that is right for your machine, the following two criteria are very important.
Criterion 1: It should be appropriate for the machine's usage environment and the operating condition that is being demanded of the bearing
Criterion 2: It should be easy to acquire replacement bearings and it should facilitate maintenance/inspection of the machine
If these criteria are met when selecting a bearing for extreme special environments, damage of the machine can be reduced, the time needed to replace the bearings when performing repairs can be shortened, and the machine can be used for a longer period of time.
The order of priority for selecting bearings for extreme special environments
Bearings for extreme special environments are to be selected in the order of priority shown in Table 1.
"How to Select the Right Bearing for Extreme Special Environments" will mainly explain about the materials and lubricants that are right for the usage environment and required properties shown in step (1).
For more information on the examination items in steps (2) to (9), please see "How to Select the Right Bearing (Part 1) to (Part 8)."
Table 1: The order of priority for selecting bearings for extreme special environments
| Order | Examination item | Major points to confirm |
| ① | Bearing materials and lubricants | What kinds of materials and lubricants are right for the usage environment and required properties? |
| ② | Bearing type | What magnitude and direction of load do you need? Will it fit in the installation space? |
| ③ | Bearing arrangement | Are you using two (or more) bearings on a single shaft? |
| ④ | Bearing dimensions and service life | Do the dimensions and service life satisfy your needs? |
| ⑤ | Bearing limiting speed, running accuracy, fits and internal clearance | Does it have the necessary running accuracy and rigidity for the machine? Does it have the fits and internal clearance to satisfy its service life?" |
| ⑥ | Bearing preload and rigidity | Does it have the necessary rigidity for the machine? |
| ⑦ | Bearing lubrication | Can the bearing rotate stably over a long period of time? |
| ⑧ | Components surrounding the bearing | What bearing surrounding structure/assembly are you looking for? |
| ⑨ | Bearing mounting and dismounting | Will it facilitate maintenance/inspection of the machine? |
See the following for details on selecting bearings.
How to Select the Right Bearing (Part 1)
3. Materials and lubricants used in bearings for extreme special environments
For the material used in bearing rings and rolling elements, high carbon chromium bearing steel, which is generally resistant to rolling fatigue, is used.
However, because environments such as clean and vacuum environments prevent the application of anti-corrosion oil to the bearings, high carbon chromium bearing steel cannot be used due to its lack of corrosion resistance.
For this reason, it is necessary to select either special steel or a ceramic material that is appropriate for the usage environment and properties.
1)Special steel
Table 2 shows the properties and appropriate usage environments of the major special steel materials used for bearings.
Table 2: The characteristics and appropriate usage environments of major special steel materials
|
Special steel |
Characteristics | Suitable environment | Remarks | ||
| Rolling fatigue strength | Low gas emission | Corrosion resistance | |||
| Martensitic stainless steela) (JIS SUS440C) |
+++ | +++ | + |
Clean |
|
| Precipitation hardening stainless steelb) (JIS SUS630) |
++ | +++ | ++ | Corrosive | Limited usage load |
| High speed tool stef elc) (JIS SKH4, AISI M50) |
+++ | +++ | - | High temperature (350°C or higher) |
|
| Non-magnetic stainless steel | ++ | +++ | + | Non-magnetic | |
| <For comparison> High carbon chromium bearing steel (JIS SUJ2) |
+++ | +++ | - | ||
* JIS (Japanese Industrial Standard)、ANSI (American National Standards Institute, Inc.)
+++ Excellent、++ Good、+ Fair、-Unacceptable
| a) | In clean and vacuum environments, anti-corrosion oil will contaminate the environment (and therefore cannot be used), so martensitic stainless steel (JIS SUS440C) is used, as it has excellent corrosion resistance. |
| b) | In highly corrosive environments, precipitation hardening stainless steel (JIS SUS630) is used, but because it has insufficient rotation fatigue resistance, there is a limit on the usage load. |
| c) | In high-temperature environments, martensitic stainless steel is used at temperatures up to 350°C. For temperatures higher than 350°C, high speed tool steel (JIS SKH4 or ANSI M50) is used. |
See the following for details on special steel.
Special steel bearings
2)Ceramic materials
Ceramic materials are excellent in vacuum, corrosive, and high-temperature environments, and also have the benefits of being both highly non-magnetic and highly insulative.
Table 3 shows the properties and appropriate usage environments of the major ceramic materials used for bearings.
Table 3: The properties and appropriate usage environments of major ceramic materials for bearings
| Ceramic material | Property | Suitable environment | Remarks | |||
| Density g/cm3 |
Rolling fatigue strength | Impact strength | Heat resistance (°C) | |||
| Silicon nitride (Si3N4) |
3.2 | +++ | +++ | 800 | Vacuum Corrosive High temperature |
|
| Zirconia (ZrO2) |
6.0 | ++ | + | 200 | Corrosive | Limited usage load |
| Silicon carbide (SiC) |
3.1 | + | + | 1,000 or higher | Corrosive Ultra-high temperature |
Limited usage load |
| <For comparison> High carbon chromium bearing steel (JIS SUJ2) |
7.8 | +++ | +++ | 180 | ||
+++ Excellent、++ Good、+ Fair
Of these ceramics, silicon nitride is the standard ceramic material used for bearings because it provides the best resistance to rolling fatigue.
See the following for details on ceramic materials.
Ceramic bearings
Since ceramic materials have a lower density than steel, there is a lower centrifugal force of the rolling elements as shown in Figure 1. This makes ceramic materials suitable for high-speed rotation.
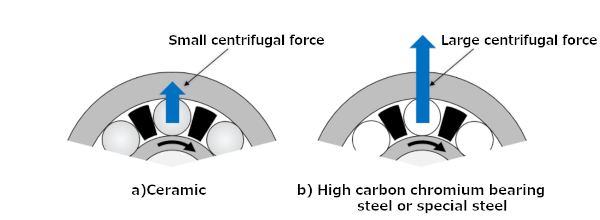
Figure 1: Centrifugal force of the rolling elements
See the following for details on the high-speed rotation performance of ceramic bearings.
Bearings that use ceramic rolling elements to achieve a faster rotation
4. Ceramic bearings
1)Ceramic bearing structure
As shown in Figure 2, ceramic bearings come in two basic types: Full Ceramic Bearings and Hybrid Ceramic Bearings. In the former, both the bearing rings and rolling elements are made of ceramic materials, whereas in the latter only the rolling elements are ceramic.
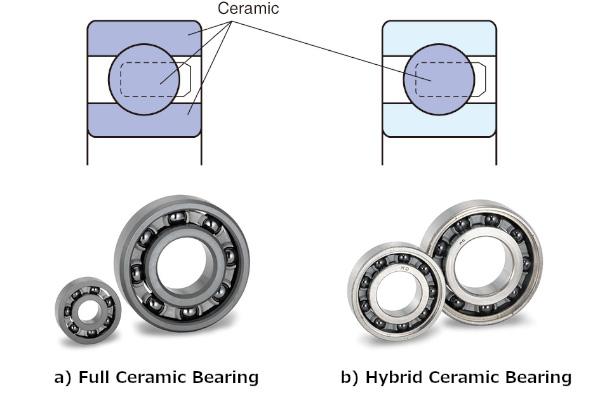
Fig. 2: Ceramic bearing structure
In Hybrid Ceramic Bearings, the inner and outer rings are made of a material that is appropriate for the application.
Metal, resin, or other materials are used for the cages of ceramic bearings depending on the usage environment and conditions.
2) Precautions regarding the use of ceramic bearings
Ceramic materials have a significantly different coefficient of linear expansion than steel materials. When using ceramic bearings, you must pay attention to their fitting and the temperature during operation.
See the following for details on the fitting of ceramic bearings.
Fitting of ceramic bearings
5. Lubricant
Lubricant plays a major role in facilitating the stable and smooth rotation of the bearing.
See the following for details on the roles of lubricants.
Purpose and method of lubrication
There are two types of lubricant used in bearings for extreme special environments: solid lubricants and grease.
1) Grease
Grease lubrication is superior to solid lubrication and is used in cases where only a very small amount of oil evaporation is acceptable.Fluorinated grease is chemically stable at low vapor pressure, and is used mainly at atmospheric temperatures of 200°C or lower.
2) Solid lubricants
Solid lubricants are used in clean, ultrahigh vacuum, and high-temperature environments (where grease cannot be used), or where oil evaporation from the grease cannot be allowed.Table 4 shows the properties and appropriate usage environments of the major solid lubricants.
Table 4: The properties and appropriate usage environments of major solid lubricants
| Type | Solid lubricant | Property | Suitable environment | |||
| Thermal stability (°C) |
Low particle emission |
Low gas emission | ||||
| Atmosphere | Vacuum | |||||
| Soft metals | Silver (Ag) |
― | 600 or higher | + | +++ | Ultrahigh vacuum environments |
| Layer lattice materials | Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) |
350 | 1,350 | + | ++ | Vacuum or high-temperature environments |
| Tungsten disulfide (WS2) |
425 | 1,350 | + | ++ | ||
| Polymeric materials | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
260 | 260 | +++ | + | Clean, vacuum, or corrosive environments |
+++ Excellent、++ Good、+ Fair
a) Soft metal-based solid lubricants
Soft metal-based lubricants are suitable for ultrahigh vacuum environments because of their low gas emission from the bearing. These lubricants are used by coating the rolling elements (see Figure 3).
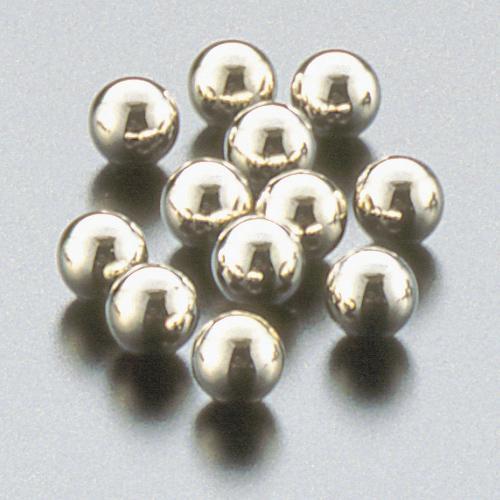

Fig. 3: Silver-coated rolling elements (balls)
b)Layer lattice-based solid lubricants
Thermally stable, layer lattice materials are well-suited to high-temperature environments. They are used by coating the bearing rings and cage, or by including them in the cage material.However, layer lattice materials emit a large amount of particles, making them unsuitable for clean environments.
c)Polymeric solid lubricants
Polymeric materials, which have low particle emission, are suitable for clean and corrosive environments, as well as for use in atmospheric and vacuum environments and with repeated usage conditions.Polymeric solid lubricants are used by coating the bearing rings and cage, or as the cage material.
See the following for details on lubricants.
Lubricants for EXSEV bearings
6. Conclusion
Materials and lubricants for bearings for extreme special environments should be selected by examining detailed operating conditions (such as temperature, load, and rotational speed) and by considering both the usage environment and required properties.
| 1) | Depending on the usage environment and required properties, bearing rings and rolling elements will be made of either high carbon chromium bearing steel, special steel, or ceramic materials.Ceramic materials are excellent in vacuum, corrosive, and high-temperature environments, and also have the benefits of being both highly non-magnetic and highly insulative. |
| 2) | Two types of lubricants are used: solid lubricants and grease.Grease lubrication has excellent lubricity and is used in cases where only a very small amount of oil evaporation is acceptable.Solid lubricants are used in environments where grease cannot be used. |
In the next column, we will discuss important points for selecting bearings for extreme special environments used in clean, vacuum, high-temperature, or corrosive environments.
JTEKT also offers a selecting tool for bearings for extreme special environments.
Selecting tool for bearings for extreme special environments
If you have any technical questions regarding bearings for extreme special environments, or opinions/thoughts on these "Bearing Trivia" pages, please feel free to contact us using the following form.