Bearing Trivia
How to Select the Right Bearing (Part 8): Bearing mounting and dismounting
- #2 How to Select the Right Bearing
In Part 7, we explained about the components surrounding the bearing.
A list of earlier "How to Select the Right Bearing" entries can be seen here
In Part 8, we will explain about bearing mounting and dismounting.
The points to consider when selecting the right bearing have been introduced in the order indicated in Table 1.
In this final part, we will introduce you to bearing mounting and dismounting.
Table 1: Bearing selection checklist
| Order | Examination item | Major points to confirm |
|---|---|---|
| ① | Bearing type | What magnitude and direction of load do you need? Will it fit in the installation space? |
| ② | Bearing arrangement | Are you using two (or more) bearings on a single shaft? |
| ③ | Bearing dimensions and service life | Do the dimensions and service life satisfy your needs? |
| ④ | Bearing limiting speed, running accuracy, fits and internal clearance | Does it have the necessary running accuracy and rigidity for the machine? |
| ⑤ | Bearing preload and rigidity | Does it have the necessary rigidity for the machine? |
| ⑥ | Bearing lubrication | Can the bearing rotate stably over a long period of time? |
| ⑦ | Components around the bearing | What bearing surrounding structure/assembly are you looking for? |
| ⑧ | Bearing mounting and dismounting |
Will it facilitate maintenance/inspection of the machine? <This is the focus of Part 8> |
This Bearing Trivia entry explains the following points with regard to mounting and dismounting bearings.
- Precautions regarding the handling of bearings
- Bearing mounting
- Bearing dismounting
- Maintenance and inspection of bearings
1. Precautions regarding the handling of bearings
Bearings are high-precision machine components. They therefore need to be handled with care.
Table 2 shows the precautions for handling of bearings.
Table 2: Precautions regarding the handling of bearings.
| number | Content | Points to be aware of |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Keeping them clean | Keep the bearing and its surrounding components clean and prevent entry of foreign matters. |
| 2 | Handling them with care | Handle using the proper tools and avoid handling roughly so as not to cause damage. |
| 3 | Rusting |
Operators should wear gloves in order not to soil bearings with perspiration from their hands. Do not handle bearings in high humidity. |
<N.B.>
Bearings are covered with proper anti-corrosion oil and wrapped in antitarnish paper before being shipped.In order to prevent rust when storing for a long time, you should store them on shelves at least 30 cm from the floor, at a humidity no higher than 65%, and at a temperature around 20°C
2. Bearing mounting
1) Recommended preparation prior to mounting
a)Preparation of bearings
Just before mounting, remove the bearings from their packaging.
Since the anti-corrosion oil covering bearings is a highly capable lubricant, the oil should not be cleaned off if the bearings are used for normal operation.
b) Preparation of shafts and housings
Perform cleaning and check whether there are flaws or burrs as a result of machining.Be particularly careful to completely remove things like casting sands and chips from inside the housing.
c) Inspection of shafts and housings
Check that the dimensions, forms, and finishes of the shaft and the housing are accurate to those specified in the design.The shaft diameter and housing bore diameter should be measured at the several points as shown in Figures 1 and 2.
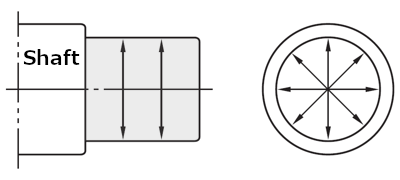
Fig. 1: Measuring points on shaft diameter
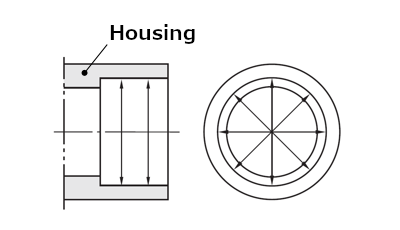
Fig. 2: Measuring points on housing bore diameter
Just before mounting the bearing, machine oil should be applied to the fitting surfaces of the shaft and housing that have passed inspection.
2) Bearing mounting
The mounting procedure depends on the type and fitting conditions of the bearing.Here we will explain about mounting a bearing by interference fit.
What is interference fit?
How to Select the Right Bearing (Part 4): Bearing limiting speed, running accuracy, and fits
Bearing Trivia for Beginners: "Fits"
Bearing mounting methods with interference fit can be by "press fit", "shrink fit", or "cooling fit" (see Table 3).
Table 3: Bearing mounting by interference fit
| Interference fit | Bearing arrangement | Tool/device used |
|---|---|---|
| inner ring | Press fit | Press |
| Bolts and nuts | ||
| Shrink fit (heat expansion) | Oil bath | |
| outer ring | Press fit | Press |
| Bolts and nuts | ||
| Cooling fit (cooling shrinkage) | Dry ice |
a) Press fit
When mounting small size bearings with restricted interference, press fit is applied.
The most widely used methods of press fit are by use of a press (see Figure 3) and use of bolts and nuts (see Figure 4).
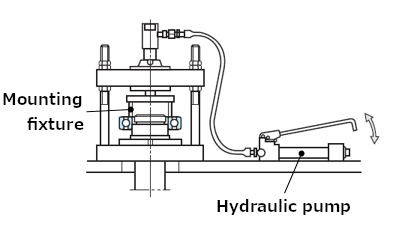
Fig. 3: Using press fit
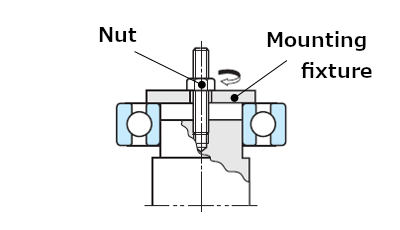
Fig. 4: Using bolts and nuts
Both of these press fit methods involve using a mounting fixture to apply force evenly to the bearing to mount it slowly with care (see Figure 5).
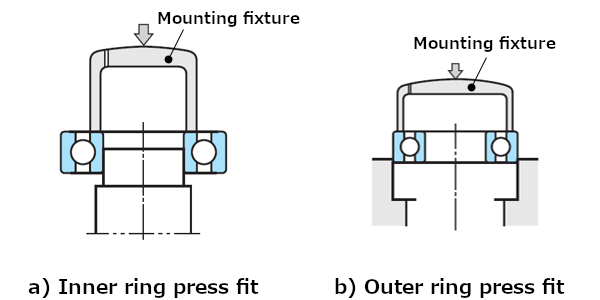 Fig. 5: Use of a mounting fixture in press fit
Fig. 5: Use of a mounting fixture in press fit
<N.B.>
- When pressing the inner ring onto the shaft, the mounting fixture cannot come in contact with the outer ring!
- When pressing the outer ring onto the housing, the mounting fixture cannot come in contact with the inner ring!
If pressure is not applied with the correct fixture position, damage will be caused to the bearing's raceway surface.
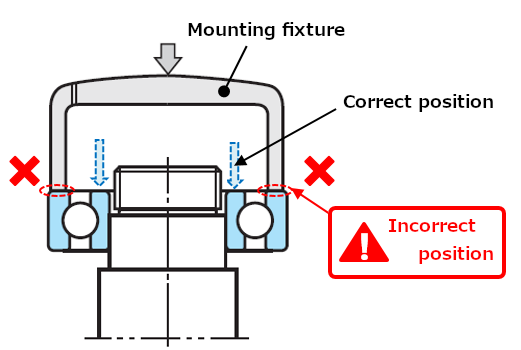
Fig. 6: Inappropriate press fit method for inner ring press fit
b) Shrink fit (interference fit of inner rings)
When mounting bearings that allow heavy interference onto a shaft or large size bearings, shrink fit is applied.Shrink fit, which expands bearings by heating them, has the advantages of not applying too much force to bearings and taking only a short time.The most typical method of shrink fit involves heating the bearing in an oil bath (see Figure 7).
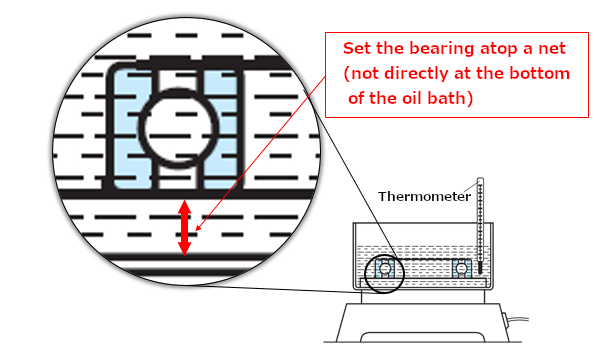
Fig. 7: Heating with an oil bath
<N.B.>
Heat the bearing at a temperature of 100°C or less.(Heating at temperatures 120°C or higher will cause the bearing to lose its hardness and result in a decrease in service life.)
c) Cooling fit (interference fit of outer rings)
This method fits bearings into housings by cooling them with dry ice or equivalent.Since moisture in the atmosphere adheres to bearings, proper rust preventive treatment is required.
3)Checking the bearing after mounting
If preload is required, apply preload to the bearing and install a sealing device.
What is a sealing device?
How to Select the Right Bearing (Part 7): Components surrounding the bearing
a) Confirmation after mounting (before test run)
With compact machines, rotation is checked by manual operation, in order to ensure that there are no abnormalities as indicated in Table 4.
Table 4: Bearing abnormalities during test run
| number | Abnormalities | Likely causes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Knocking (non-smooth rotation) | Entry of foreign matter, flaws on rolling contact surfaces |
| 2 |
Heavy load hinders rotation (excessive torque) |
Friction on sealing devices, clearances that are too small, mounting (installation) errors |
| 3 | Uneven running torque | Improper mounting, mounting (installation) errors"mounting (installation) errors" |
For large machines where manual operation is not possible, idle rotation of the bearing is performed under no load by turning off the power source immediately after turning it on. This allows us to check that there is no abnormal vibration or noise.
b) Confirmation during test run
When performing the test run with a driving force, start under no load and at low speed, before gradually increasing to the specified conditions.Check the noise, increase in temperature and vibration, and, if any abnormalities occur, perform inspection promptly.Bearings may be dismounted as necessary in order to perform the inspection.
Please click the link below for more detailed information on the causes and countermeasures for cases of noise or increase in temperature.re.
3. Bearing dismounting
When dismounting a bearing for reuse or to find the causes of damage, just as when mounting, it is important to take care not to damage the bearing or the surrounding components.Since bearings mounted by interference fit are especially easily damaged during dismounting, it is particularly important to take care not to damage them.
Table 5 indicates the procedure for dismounting an interference fitted bearing.
Table 5: Procedure for dismounting an interference fitted bearing
| Interference fit | Dismounting methods | Tool/device used |
|---|---|---|
| inner ring | Mechanical | Press |
| Special tools | ||
| outer ring | Mechanical | Notches for dismounting |
| Bolts and nuts |
1) Inner ring dismounting methods
Some typical methods of dismounting the inner ring are the method that uses a press and the method that uses special tools.
a) Dismounting by use of a press
If it is possible to perform dismounting by use of a press (see Figure 8), this is the simplest method.Force is applied to the inner ring using the dismounting fixture.
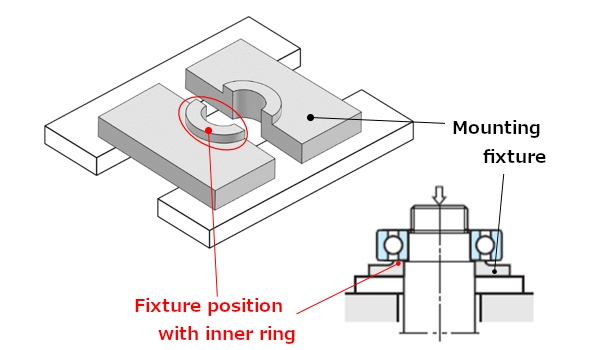
Fig. 8: Dismounting by use of a press
<N.B.>
When dismounting the inner ring, make sure that the dismounting fixture does not come in contact with the outer ring.If the dismounting fixture comes in contact with the outer ring, damage will be caused to the bearing's raceway surface.
b) Dismounting by use of special tools
When dismounting with special tools (see Figure 9), the jaws of the tool should firmly hold the side of the inner ring.
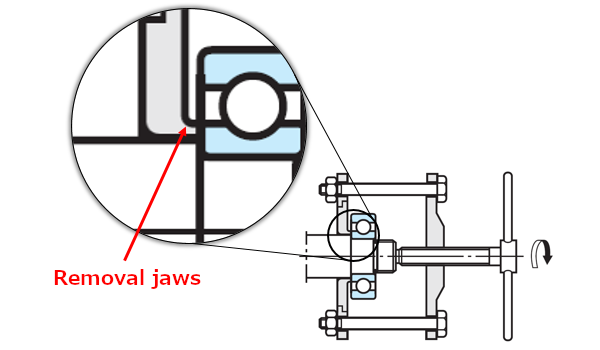 Fig. 9: Dismounting by use of special tools
Fig. 9: Dismounting by use of special tools
2) Outer ring dismounting methods
To perform dismounting of an outer ring with interference fit, notches (see Figure 10) or bolt holes (see Figure 11) should be provided on the housing shoulder.
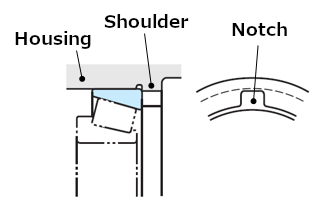 Fig. 10: Notch for dismounting
Fig. 10: Notch for dismounting
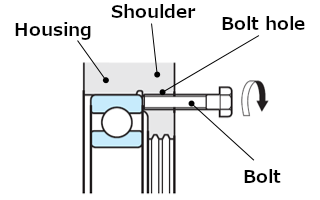 Fig. 11: Bolt and bolt hole for dismounting
Fig. 11: Bolt and bolt hole for dismounting
4. Maintenance and inspection of bearings
Early detection of failures and prevention of sudden damage to the machine, through periodic and proper maintenance and inspection of the bearings, are very important for the enhancement of productivity and profitability.Table 6 indicates the procedure for handling dismounted bearings.
Table 6: Handling of dismounted bearings
| Order | What to do | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Take photographs to record physical condition | |
| 2 | Check how much lubricant is remaining and collect a sample for inspection | |
| 3 | Clean and perform rust preventive treatment | Perform rough cleaning and finish cleaning to remove clinging matter |
| 4 | Inspect | Dimensional and running accuracy, internal clearance, fitting surfaces, raceways, seals, and so on |
| 5 | Make decision to reuse or not | Consider the performance and importance of the machine, and the frequency of inspection. |
1) Bearing inspection
Inspection should be performed while closely monitoring the dimensional and running accuracy, internal clearance, fitting surfaces, raceways, seals, and so on.
2) Decision on the reuse of bearings
It is desirable for skilled persons who have sufficient knowledge of bearings and the handling thereof to make decisions on the reuse of bearings.
he criteria for determining whether reuse is possible or not vary depending on the performance and importance of the machine and the frequency of inspection.
Examples of bearing failures are useful in deciding whether to reuse a dismounted bearing.
Please click the link below for more detailed information on examples of bearing failures:
Examples of bearing failures - Ball & Roller Bearings Catalog
Conclusion
In order to ensure the intended performance of the machine, a bearing appropriate to the usage conditions should be selected.
- Mount the bearing by the method appropriate to the type and fitting conditions of the bearing.Take particular care, when mounting a bearing with interference fit, not to damage the bearing and surrounding components.
- Perform a test run of the machine after mounting the bearing, and check that there are no abnormalities such as noise, increase in temperature, or vibration.
- It is very important for the enhancement of productivity and profitability to perform periodic and proper maintenance and inspection of the bearing to preventi sudden machine breakdown.
- Dismount in such a manner that neither the bearing nor the surrounding components are damaged, and inspect the dismounted bearing with great care to ensure there are no abnormalities.If an abnormality is found, reaffirm that the bearing is suited to the surrounding components, the lubrication method, and the usage conditions, and then implement the appropriate countermeasures to improve the reliability of the machine.
Over the course of these eight trivia column, we have explained the key points for selecting the type of bearing.
We hope that these "Bearing Trivia" pages will be useful for those who build machines and perform maintenance and inspection of bearings.
If you have any technical questions regarding bearings, or opinions/thoughts on these "Bearing Trivia" pages, please feel free to contact us using the following form.