As described in Section 9-3, the characteristics / magnitude of the bearing load, temperature, mounting / dismounting methods and other conditions must be considered to choose proper fits.
Past experience is also valuable.
Table 9-3 shows standard fits for the metric series bearings; Tables 9-4 to 9-8 tabulate the most typical and recommended fits for different bearings types.
『Table 9-4 (1) Recommended shaft fits for radial bearings (classes 0, 6X, 6)』
『Table 9-4 (2) Recommended housing fits for radial bearings (classes 0, 6X, 6)』
『Table 9-5 (1) Recommended shaft fits for precision extra-small/miniature ball bearings (d<10mm)』
『Table 9-5 (2) Recommended housing fits for precision extra-small/miniature ball bearings (D≦30mm)』
『Table 9-6 (1) Recommended shaft fits for metric J series tapered roller bearings』
『Table 9-6 (2) Recommended housing fits for metric J series tapered roller bearings』
『Table 9-7 (1) Recommended shaft fits for inch series tapered roller bearings』
『Table 9-7 (2) Recommended housing fits for inch series tapered roller bearings』
『Table 9-8 (1) Recommended shaft fits for thrust bearings (classes 0, 6)』
『Table 9-8 (2) Recommended housing fits for thrust bearings (classes 0, 6)』
Table 9-3 Standard fits for metric series bearings1)
(1) Fits for bore diameter 2) of radial bearings
| Class of bearing | Rotating inner ring load or indeterminate direction load | Stationary inner ring load | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class of shaft tolerance range | ||||||||||
| Classes 0, 6X, 6 | r 6 | p 6 | n 6 | m 6 | k 6 | js 6 | h 5 | h 6 | g 6 | f 6 |
| m 5 | k 5 | js 5 | h 5 | g 5 | ||||||
| Class 5 | - | - | - | m 5 | k 4 | js 4 | h 4 | h 5 | - | - |
| Fit | Interference fit | Transition fit | Clearance fit | |||||||
(2) Fits for outside diameter 2) of radial bearings
| Class of bearing | Stationary outer ring load | Indeterminate direction load or rotating outer ring load | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class of housing bore tolerance range | |||||||||
| Classes 0, 6X, 6 | G 7 | H 7 | JS 7 | - | JS 7 | K 7 | M 7 | N 7 | P 7 |
| H 6 | JS 6 | JS 6 | K 6 | M 6 | N 6 | ||||
| Class 5 | - | H 5 | JS 5 | K 5 | - | K 5 | M 5 | - | - |
| Fit | Clearance fit | Transition fit | Interference fit | ||||||
(3) Fits for bore diameter 2) of thrust bearings
| Class of bearing | Central axial load (generally for thrust bearings) | Combined load (in the case of spherical thrust roller bearing) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotating shaft race load or indeterminate direction load | Stationary shaft race load | |||||
| Class of shaft tolerance range | ||||||
| Classes 0, 6 | js 6 | h 6 | n 6 | m 6 | k 6 | js 6 |
| はめあい | Transition fit | Interference fit | Transition fit | |||
(4) Fits for outside diameter 2) of thrust bearings
| Class of bearing | Central axial load (generally for thrust bearings) | Combined load (in the case of spherical thrust roller bearing) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stationary housing race load or indeterminate direction load | Rotating housing race load | ||||||
| Class of housing bore tolerance range | |||||||
| Classes 0, 6 | - | H 8 | G 7 | H 7 | JS 7 | K 7 | M 7 |
| Fit | Clearance fit | Transition fit | |||||
[Notes]
1) Bearings specified in JIS B 1512
2) Follow JIS B 1514-1 and 1514-2 for tolerance.
Table 9-4 (1) Recommended shaft fits for radial bearings (classes 0, 6X, 6)
| Conditions1) | Ball bearing | Cylindrical roller bearing Tapered roller bearing | Spherical roller bearing | Class of shaft tolerance range | Remarks | Applicationsv(for reference) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaft diameter (mm) | ||||||||||
| over | up to | over | up to | over | up to | |||||
| Cylindrical bore bearing (classes 0, 6X, 6) | ||||||||||
| Rotating inner ring load or indeterminate direction load | Light load or fluctuating load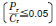 |
- | 18 | - | - | - | - | h 5 | For applications requiring high accuracy, js 5,k 5 and m 5 should be used in place of js 6, k 6 and m 6. | Electric appliances, machine tools, pumps, blowers, carriers etc. |
| 18 | 100 | - | 40 | - | - | js 6 | ||||
| 100 | 200 | 40 | 140 | - | - | k 6 | ||||
| - | - | 140 | 200 | - | - | m 6 | ||||
Normal load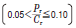 |
- | 18 | - | - | - | - | js 5 | For single-row tapered roller bearings and angular contact ball bearings, k 5 and m 5 may be replaced by k 6 and m 6, because internal clearance reduction due to fit need not be considered. | Electric motors, turbines, internal combustion engines, woodworking machines etc. |
|
| 18 | 100 | - | 40 | - | 40 | k 5 | ||||
| 100 | 140 | 40 | 100 | 40 | 65 | m 5 | ||||
| 140 | 200 | 100 | 140 | 65 | 100 | m 6 | ||||
| 200 | 280 | 140 | 200 | 100 | 140 | n 6 | ||||
| - | - | 200 | 400 | 140 | 280 | p 6 | ||||
| - | - | - | - | 280 | 500 | r 6 | ||||
Heavy load or impact load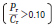 |
- | - | 50 | 140 | 50 | 100 | n 6 | Bearings with larger internal clearance than standard are required. | Railway rolling stock axle journals, traction motors |
|
| - | - | 140 | 200 | 100 | 140 | p 6 | ||||
| - | - | 200 | - | 140 | 200 | r 6 | ||||
| Stationary inner ring load | Inner ring needs to move smoothly on shaft. | All shaft diameters | g 6 | For applications requiring high accuracy, g 5 should be used. For large size bearing, f 6 may be used for easier movement. |
Stationary shaft wheels | |||||
| Inner ring does not need to move smoothly on shaft. | All shaft diameters | h 6 | For applications requiring high accuracy, h 5 should be used. | Tension pulleys, rope sheaves etc. |
||||||
| Central axial load only | All shaft diameters | js 6 | - | - | ||||||
| Tapered bore bearing (class 0) (with adapter or withdrawal sleeve) | ||||||||||
| All loads | All shaft diameters | h 9/IT 5 2) | For transmission shafts, h10/IT72) may be applied. | |||||||
[Notes]
1) Light, normal, and heavy loads refer to those with dynamic equivalent radial loads (Pr) of 5 % or lower, over 5 % up to 10 % inclusive, and over 10 % respectively in relation to the basic dynamic radial load rating (Cr) of the bearing concerned.
2) IT 5 and IT 7 mean that shaft roundness tolerance, cylindricity tolerance, and other errors in terms of shape should be within the tolerance range of IT 5 and IT 7, respectively. For numerical values for standard tolerance grades IT 5 and IT 7, refer to supplementary table at end of this catalog.
[Remark]This table is applicable to solid steel shafts.
Table 9-4 (2) Recommended housing fits for radial bearings (classes 0, 6X, 6)
| Conditions | Class of housing bore tolerance range | Remarks | Applications (for reference) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Housing | Load type etc.1) | Outer ring axial displacement2) | ||||
| One-piece or split type | Stationary outer ring load | All load types | Easily displaceable | H 7 | G 7 may be applied when a large size bearing is used, or if the temperature difference is large between the outer ring and housing. | Ordinary bearing devices, railway rolling stock axle boxes, power transmission equipment etc. |
| Light or normal load | Easily displaceable | H 8 | - | |||
| High temperature at shaft and inner ring | Easily displaceable | G 7 | F 7 may be applied when a large size bearing is used, or if the temperature difference is large between the outer ring and housing. | Drying cylinders etc. | ||
| One-piece type | Light or normal load, requiring high running accuracy | Not displaceable in principle | K 6 | Mainly applied to roller bearings. | ||
| Displaceable | JS 6 | Mainly applied to ball bearings. | ||||
| Requiring low-noise rotation | Easily displaceable | H 6 | - | |||
| Indeterminate direction load | Light or normal load | Normally displaceable | JS 7 | For applications requiring high accuracy, JS 6 and K 6 should be used in place of JS 7 and K 7. | Electric motors, pumps, crankshaft main bearings etc. | |
| Normal or heavy load | Not displaceable in principle | K 7 | ||||
| High impact load | Not displaceable | M7 | - | Traction motors etc. | ||
| Rotating outer ring load | Light or fluctuating load | Not displaceable | M7 | - | Conveyor rollers, ropeways, tension pulleys etc. | |
| Normal or heavy load | Not displaceable | N7 | Mainly applied to ball bearings. | Wheel hubs with ball bearings etc. | ||
| Thin section housing, heavy or high impact load | Not displaceable | P7 | Mainly applied to roller bearings. | Wheel hubs with roller bearings, bearings for large end of connecting rods etc. | ||
[Notes]
1) Loads are classified as stated in Note 1) to Table 9-4 (1).
2) Indicating distinction between applications of non-separable bearings permitting and not permitting axial displacement of the outer rings.
[Remarks]
1. This table is applicable to cast iron or steel housings.
2. If only central axial load is applied to the bearing, select such tolerance range class as to provide clearance in the radial direction for outer ring.
Table 9-5 (1) Recommended shaft fits for precision extra-small/miniature ball bearings (d<10mm)
| Load type | Bearing tolerance class | Single plane mean bore diameter deviationΔdmp | Shaft diameter dimensional tolerance | Fit1) | Applications | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| upper | lower | upper | lower | |||||
| Rotating inner ring load | Middle/high speed Light or normal load | ABMA5P | 0 | -5.1 | +2.5 | -2.5 | 7.6T~2.5L | Gyro rotors, air cleaners, electric tools, encoders |
| JIS class 5 | 0 | -5 | 7.5T~2.5L | |||||
| ABMA7P | 0 | -5.1 | +2.5 | -2.5 | 7.6T~2.5L | |||
| JIS class 4 | 0 | -4 | 6.5T~2.5L | |||||
| Low speed Light load | ABMA5P | 0 | -5.1 | -2.5 | -7.5 | 2.6T ~7.5L | Gyro gimbals, synchronizers, servomotors, floppy disc spindles | |
| JIS class 5 | 0 | -5 | 2.5T~7.5L | |||||
| ABMA7P | 0 | -5.1 | -2.5 | -7.5 | 2.6T~7.5L | |||
| JIS class 4 | 0 | -4 | 1.5T~7.5L | |||||
| Rotating outer ring load | Low to high speed Light load | ABMA5P | 0 | -5.1 | -2.5 | -7.5 | 2.6T~7.5L | Pinch rolls, tape guide rollers, linear actuators |
| JIS class 5 | 0 | -5 | 2.5T~7.5L | |||||
| ABMA7P | 0 | -5.1 | -2.5 | -7.5 | 2.6T~7.5L | |||
| JIS class 5 | 0 | -4 | 1.5T ~7.5L | |||||
[Note]1) Symbols T and L means interference and clearance respectively.
Table 9-5 (2) Recommended housing fits for precision extra-small/miniature ball bearings (D≦30mm)
| Load type | Bearing tolerance class | Single plane mean outside diameter deviationΔdmp | Housing bore diameter dimensional tolerance | Fit1) | Applications | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| upper | lower | upper | lower | |||||
| Rotating inner ring load | Middle/high speed Light or normal load |
ABMA 5P | 0 | -5.1 | +5 | 0 | 0~10.1L | Gyro rotors, air cleaners, electric tools, encoders |
| ABMA 7P | ||||||||
| JIS class 52) | 0 | -5 | +5 | 0 | 0~10 L | |||
| 0 | -6 | 0~11 L | ||||||
| JIS class 42) | 0 | -4 | +5 | 0 | 0~ 9 L | |||
| 0 | -5 | 0~10 L | ||||||
| Low speed Light load |
ABMA 5P | 0 | -5.1 | +2.5 | -2.5 | 2.5T~7.6L | Gyro gimbals, synchronizers, servomotors, floppy disc spindles | |
| ABMA 7P | ||||||||
| JIS class 52) | 0 | -5 | +2.5 | -2.5 | 2.5T~7.5L | |||
| 0 | -6 | 2.5T ~8.5L | ||||||
| JIS class 42) | 0 | -4 | +2.5 | -2.5 | 2.5T~6.5L | |||
| 0 | -5 | 2.5T~7.5L | ||||||
| Rotating outer ring load | Rotating outer ring load | ABMA 5P | 0 | -5.1 | +2.5 | -2.5 | 2.5T~7.6L | Pinch rolls, tape guide rollers |
| ABMA 7P | ||||||||
| JIS class 52) | 0 | -5 | +2.5 | -2.5 | 2.5T~7.5L | |||
| 0 | -6 | 2.5T~8.5L | ||||||
| JIS class 42) | 0 | -4 | +2.5 | -2.5 | 2.5T~6.5L | |||
| 0 | -5 | 2.5T~7.5L | ||||||
[Notes]
1) Symbols T and L means interference and clearance respectively.
2) In the columns "single plane mean outside diameter deviation" and "fit" upper row values are applied in the case of D≦18mm, lower row values in the case of 18 < <D≦30mm.
Table 9-6 (1) Recommended shaft fits for metric J series tapered roller bearings
Bearing tolerance : class PK, class PN
| Load type | Nominal bore diameter d mm | Class of shaft tolerance range | Remarks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| over | up to | ||||
| Rotating inner ring load | Normal load | 10 | 120 | m 6 | |
| 120 | 500 | n 6 | |||
| Heavy load Impact load High speed rotation |
10 | 120 | n 6 | Generally, bearing internal clearance should be larger than standard. | |
| 120 | 180 | p 6 | |||
| 180 | 250 | r 6 | |||
| 250 | 500 | r 7 | |||
| Rotating outer ring load | Normal load without impact | 80 | 315 | h 6 or g 6 | |
| Heavy load Impact load High speed rotation | 10 | 120 | n 6 | Generally, bearing internal clearance should be larger than standard. | |
| 120 | 180 | p 6 | |||
| 180 | 250 | r 6 | |||
| 250 | 500 | r 7 | |||
Bearing tolerance : class PC, class PB
| Load type | Nominal bore diameter d mm | Class of shaft tolerance range | Remarks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (bearing tolerance class) | ||||||
| over | up to | PC | PB | |||
| Rotating inner ring load | Spindles of precision machine tools | 10 | 315 | k 5 | k 5 | |
| 315 | 500 | k 5 | - | |||
| Heavy load Impact load High speed rotation | 10 | 18 | m 6 | m 5 | Generally, bearing internal clearance should be larger than standard. | |
| 18 | 50 | m 5 | m 5 | |||
| 50 | 80 | n 5 | n 5 | |||
| 80 | 120 | n 5 | n 4 | |||
| 120 | 180 | p 4 | p 4 | |||
| 180 | 250 | r 4 | r 4 | |||
| 250 | 315 | r 5 | r 4 | |||
| 315 | 500 | r 5 | - | |||
| Rotating outer ring load | Spindles of precision machine tools | 10 | 315 | k 5 | k 5 | |
| 315 | 500 | k 5 | - | |||
Table 9-6 (2) Recommended housing fits for metric J series tapered roller bearings
Bearing tolerance : class PK, class PN
| Load type | Nominal outside diameter d mm | Class of housing bore diameter tolerance range | Remarks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| over | up to | ||||
| Rotating inner ring load | Used for free or fixed side | 18 | 315 | G 7 | Outer ring is easily displaceable in axial direction. |
| 315 | 400 | F 6 | |||
| Position of outer ring is adjustable (in axial direction) | 18 | 400 | J 7 | Outer ring is displaceable in axial direction. | |
| Position of outer ring is not adjustable (in axial direction) | 18 | 400 | P 7 | Outer ring is fixed in axial direction. | |
| Rotating outer ring load | Position of outer ring is not adjustable (in axial direction) | 18 | 120 | R 7 | Outer ring is fixed in axial direction. |
| 120 | 180 | ||||
| 180 | 400 | ||||
Bearing tolerance : class PC, class PB
| Load type | Nominal outside diameter d mm | Class of housing bore diameter tolerance range | Remarks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (bearing tolerance class) | ||||||
| over | up to | PC | PB | |||
| Rotating inner ring load | Used for free side | 18 | 315 | G 5 | G 5 | Outer ring is easily displaceable in axial direction. |
| 315 | 500 | G 5 | - | |||
| Used for fixed side | 18 | 315 | H 5 | H 4 | Outer ring is displaceable in axial direction. | |
| 315 | 500 | H 5 | - | |||
| Position of outer ring is adjustable (in axial direction) | 18 | 120 | K 5 | K 5 | Outer ring is fixed in axial direction. | |
| 120 | 180 | JS 6 | JS 6 | |||
| 180 | 250 | JS 6 | JS 5 | |||
| 250 | 315 | K 5 | JS 5 | |||
| 315 | 500 | K 5 | - | |||
| Position of outer ring is not adjustable (in axial direction) | 18 | 315 | N 5 | M 5 | Outer ring is fixed in axial direction. | |
| 315 | 500 | N 5 | - | |||
| Rotating outer ring load | Position of outer ring is not adjustable (in axial direction) | 18 | 250 | N 6 | N 5 | Outer ring is fixed in axial direction. |
| 250 | 315 | N 5 | N 5 | |||
| 315 | 500 | N 5 | - | |||
Table 9-7 (1) Recommended shaft fits for inch series tapered roller bearings
Bearing tolerance : class 4, class 2
| Load type | Nominal outside diameter d mm(1/25.4) | Deviation of a single bore diameter Δds , µm | Dimensional tolerance of shaft diameter µm | Remarks | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| over | up to | upper | lower | upper | lower | |||
| Rotating inner ring load | Normal load | - | 76.2(3.0) | +13 | 0 | +38 | +25 | |
| 76.2(3.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +25 | 0 | +64 | +38 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +51 | 0 | +127 | +76 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +76 | 0 | +190 | +114 | |||
| Heavy load Impact load High speed rotation |
- | 76.2(3.0) | +13 | 0 | Should be such that average interference stands at 0.0005×d(mm) | Generally, bearing internal clearance should be larger than standard. | ||
| 76.2(3.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +25 | 0 | |||||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +51 | 0 | |||||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +76 | 0 | |||||
| Rotating outer ring load | Normal load without impact | - | 76.2(3.0) | +13 | 0 | +13 | 0 | |
| 76.2(3.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +25 | 0 | +25 | 0 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +51 | 0 | +51 | 0 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +76 | 0 | +76 | 0 | |||
| Normal load without impact | - | 76.2(3.0) | +13 | 0 | 0 | -13 | Inner ring is displaceable in axial direction. | |
| 76.2(3.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +25 | 0 | 0 | -25 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +51 | 0 | 0 | -51 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +76 | 0 | 0 | -76 | |||
| Heavy load Impact load High speed rotation |
- | 76.2(3.0) | +13 | 0 | Should be such that average interference stands at 0.0005×d(mm) | Generally, bearing internal clearance should be larger than standard. | ||
| 76.2(3.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +25 | 0 | |||||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +51 | 0 | |||||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +76 | 0 | |||||
Bearing tolerance : class 3, class 01)
| Load type | Nominal outside diameter d mm(1/25.4) | Deviation of a single bore diameter Δds , µm | Dimensional tolerance of shaft diameter µm | Remarks | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| over | up to | upper | lower | upper | lower | |||
| Rotating inner ring load | Spindles of precision machine tools | - | 76.2(3.0) | +13 | 0 | +30 | +18 | |
| 76.2(3.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +13 | 0 | +30 | +18 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +25 | 0 | +64 | +38 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +38 | 0 | +102 | +64 | |||
| Heavy load Impact load High speed rotation |
- | 76.2(3.0) | +13 | 0 | Should be such that average interference stands at 0.0005×d(mm) | Generally, bearing internal clearance should be larger than standard. | ||
| 76.2(3.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +13 | 0 | |||||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +25 | 0 | |||||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +38 | 0 | |||||
| Rotating outer ring load | Spindles of precision machine tools | - | 76.2(3.0) | +13 | 0 | +30 | +18 | |
| 76.2(3.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +13 | 0 | +30 | +18 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +25 | 0 | +64 | +38 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +38 | 0 | +102 | +64 | |||
[Note]1) Class 0 bearing : d≦304.8mm
Table 9-7 (2) Recommended housing fits for inch series tapered roller bearings
Bearing tolerance : class 4, class 2
| Load type | Nominal outside diameter D mm(1/25.4) | Deviation of a single outside diameter ΔDs , µm | Dimensional tolerance of housing bore diameter µm | Remarks | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| over | up to | upper | lower | upper | lower | |||
| Rotating inner ring load | Used for free or fixed side. | - | 76.2(3.0) | +25 | 0 | +76 | +51 | Outer ring is easily displaceable in axial direction. |
| 76.2(3.0) | 127.0(5.0) | +25 | 0 | +76 | +51 | |||
| 127.0(5.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +25 | 0 | +76 | +51 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +51 | 0 | +152 | +102 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +76 | 0 | +229 | +152 | |||
| Position of outer ring is adjustable (in axial direction). | - | 76.2(3.0) | +25 | 0 | +25 | 0 | Outer ring is displaceable in axial direction. | |
| 76.2(3.0) | 127.0(5.0) | +25 | 0 | +25 | 0 | |||
| 127.0(5.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +25 | 0 | +51 | 0 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +51 | 0 | +76 | +25 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +76 | 0 | +127 | +51 | |||
| Position of outer ring is not adjustable (in axial direction). | - | 76.2(3.0) | +25 | 0 | -13 | -38 | Outer ring is fixed in axial direction. | |
| 76.2(3.0) | 127.0(5.0) | +25 | 0 | -25 | -51 | |||
| 127.0(5.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +25 | 0 | -25 | -51 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +51 | 0 | -25 | -76 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +76 | 0 | -25 | -102 | |||
| Rotating outer ring load | Position of outer ring is not adjustable (in axial direction). | - | 76.2(3.0) | +25 | 0 | -13 | -38 | Outer ring is fixed in axial direction. |
| 76.2(3.0) | 127.0(5.0) | +25 | 0 | -25 | -51 | |||
| 127.0(5.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +25 | 0 | -25 | -51 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +51 | 0 | -25 | -76 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +76 | 0 | -25 | -102 | |||
Bearing tolerance : class 3, class 01)
| Load type | Nominal outside diameter D mm(1/25.4) | Deviation of a single outside diameter ΔDs , µm | Dimensional tolerance of housing bore diameter µm | Remarks | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| over | up to | upper | lower | upper | lower | |||
| Rotating inner ring load | Used for free side. | - | 152.4(6.0) | +13 | 0 | +38 | +25 | Outer ring is easily displaceable in axial direction. |
| 152.4(6.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +13 | 0 | +38 | +25 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +25 | 0 | +64 | +38 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +38 | 0 | +89 | +51 | |||
| Used for fixed side. | - | 152.4(6.0) | +13 | 0 | +25 | +13 | Outer ring is displaceable in axial direction. | |
| 152.4(6.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +13 | 0 | +25 | +13 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +25 | 0 | +51 | +25 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +38 | 0 | +76 | +38 | |||
| Position of outer ring is adjustable (in axial direction). | - | 152.4(6.0) | +13 | 0 | +13 | 0 | Position of outer ring is not adjustable (in axial direction). | |
| 152.4(6.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +13 | 0 | +25 | 0 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +25 | 0 | +25 | 0 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +38 | 0 | +28 | 0 | |||
| Position of outer ring is not adjustable (in axial direction). | - | 152.4(6.0) | +13 | 0 | 0 | -13 | Outer ring is fixed in axial direction. | |
| 152.4(6.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +13 | 0 | 0 | -25 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +25 | 0 | 0 | -25 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +38 | 0 | 0 | -38 | |||
| Rotating outer ring load | Position of outer ring is not adjustable (in axial direction). | - | 152.4(6.0) | +13 | 0 | -13 | -25 | Outer ring is fixed in axial direction. |
| 152.4(6.0) | 304.8(12.0) | +13 | 0 | -13 | -38 | |||
| 304.8(12.0) | 609.6(24.0) | +25 | 0 | -13 | -38 | |||
| 609.6(24.0) | 914.4(36.0) | +38 | 0 | -13 | -51 | |||
[Note]1) Class 0 bearing : D≦304.8mm
Table 9-8 (1) Recommended shaft fits for thrust bearings (classes 0, 6)
| Load type | Shaft diameter, mm | Class of shaft tolerance range | Remarks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| over | up to | ||||
| Central axial load (generally for thrust bearings) |
All shaft diameters | js 6 | h 6 may also be used. | ||
| Combined load (spherical thrust roller bearing) |
Stationary shaft race load | All shaft diameters | js 6 | - | |
| Rotating shaft race load or indeterminate direction load | - | 200 | k 6 | js 6, k 6 and m 6 may be used in place of k 6, m 6 and n 6, respectively. | |
| 200 | 400 | m 6 | |||
| 400 | - | n 6 | |||
Table 9-8 (2) Recommended housing fits for thrust bearings (classes 0, 6)
| Load type | Class of housing bore diameter tolerance range | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central axial load (generally for thrust bearings) |
- | Select such tolerance range class as provides clearance in the radial direction for housing race. | |
| H 8 | In case of thrust ball bearings requiring high accuracy. | ||
| Combined load (spherical thrust roller bearing) |
Stationary housing race load | H 7 | - |
| Indeterminate direction load or rotating housing race load | K 7 | In case of application under normal operating conditions. | |
| M 7 | In case of comparably large radial load. | ||
[Remark]This table is applicable to cast iron or steel housings.